Difference between revisions of "San Francisco"
(→Shopping) |
(→The Baronies: Undead Territories) |
||
| Line 1,902: | Line 1,902: | ||
== '''The Baronies''': ''Undead Territories'' == | == '''The Baronies''': ''Undead Territories'' == | ||
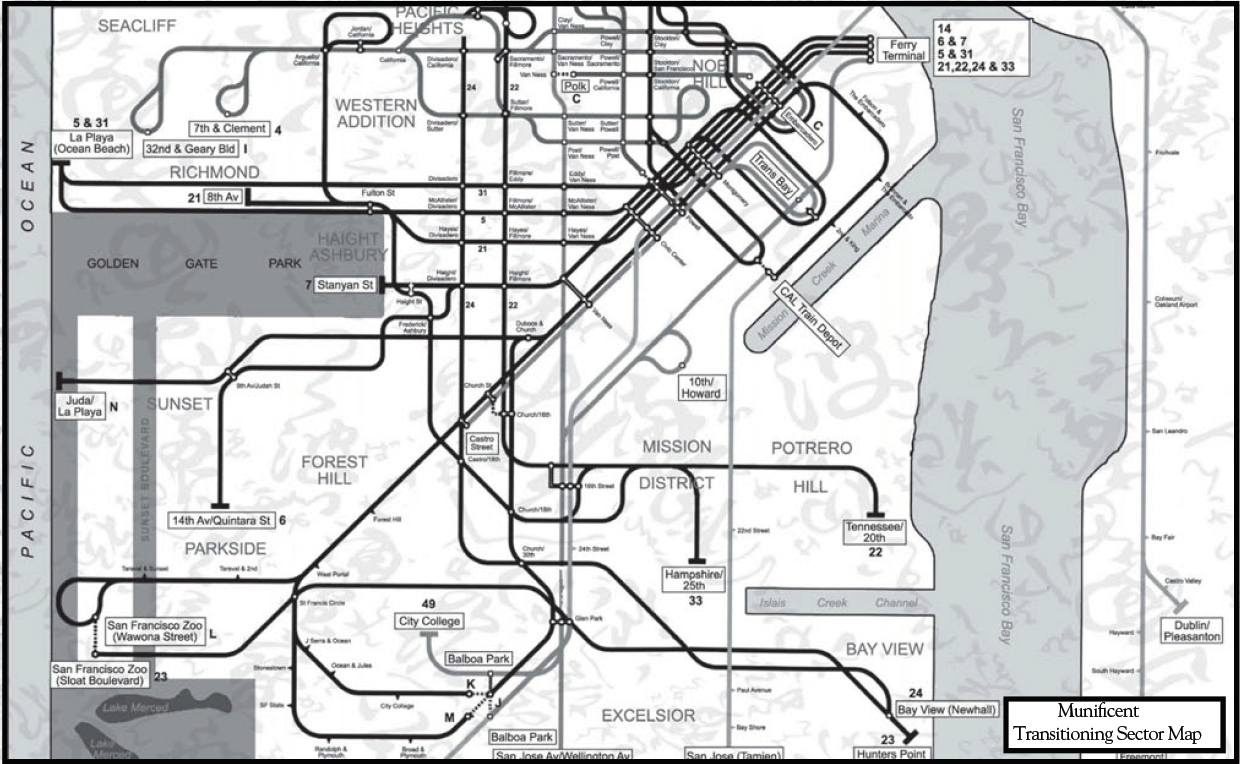
| − | [[File:San Francisco Baronies of the Undead.jpg]] | + | [[File:San Francisco Baronies of the Undead.jpg|600px]] |
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 20:35, 31 May 2022
Contents
- 1 Quote
- 2 Appearance
- 3 City Device
- 4 Climate
- 5 Demonym
- 6 Economy
- 7 Geography
- 8 Introduction
- 9 History
- 10 Attractions and Characteristics
- 11 Gentrification
- 12 Murals
- 13 Crime
- 14 Social Issues
- 15 Social Services
- 16 Culture
- 17 Parks and Recreation
- 18 Renaming Attempt
- 19 History
- 19.1 The Earliest Days
- 19.2 Exploration & Settlement
- 19.3 Independence & Growth
- 19.4 Gum San: The Golden Mountain
- 19.5 A Land of New Promise
- 19.6 East Meets West
- 19.7 Shadow Plays
- 19.8 Public Vigilance
- 19.9 Paths of Iron
- 19.10 The Dragon Thrashes its Tail
- 19.11 For Their Own Protection
- 19.12 THE GREAT LEAP OUTWARD
- 19.13 FIVE YEARS GONE
- 20 Population
- 21 Arenas
- 22 Attractions
- 23 Bars and Clubs
- 24 Cemeteries
- 25 City Government
- 26 Crime
- 27 Citizens of the City
- 28 Culture of the City
- 29 Current Events
- 30 Fortifications
- 31 Galleries
- 32 Holy Ground
- 33 Hospitals
- 34 Hotels & Hostels
- 35 Landmarks
- 36 Maps
- 37 Mass Media
- 38 Missives
- 39 Monuments
- 40 Museums
- 41 Newspapers
- 42 Parks
- 43 Private Residences
- 44 Restaurants
- 45 Ruins
- 46 Schools
- 47 Shopping
- 48 Strange Objects
- 49 Telecommunications
- 50 Theaters
- 51 Transportation
- 52 Warehouses
- 53 Mages
- 54 Vampires of the City
- 55 Vox Deorum
- 56 Deceased or Missing
- 57 The Baronies: Undead Territories
- 58 Coteries of San Francisco
- 59 Websites
- 60 Errata
Quote
"San Francisco is 49 square miles surrounded by reality." -- Paul Kantner of Jefferson Starship
"May you live in interesting times." — Chinese curse
Appearance

"No city invites the heart to come to life as San Francisco does. Arrival in San Francisco is an experience in living." -- William Saroyan, Armenian-American novelist
City Device
Climate
San Francisco has a warm-summer Mediterranean climate (Köppen Csb) characteristic of California's coast, with moist mild winters and dry summers. San Francisco's weather is strongly influenced by the cool currents of the Pacific Ocean on the west side of the city, and the water of San Francisco Bay to the north and east. This moderates temperature swings and produces a remarkably mild year-round climate with little seasonal temperature variation.
Fog is a regular feature of San Francisco summers.
Among major U.S. cities, San Francisco has the coolest daily mean, maximum, and minimum temperatures for June, July, and August. During the summer, rising hot air in California's interior valleys creates a low pressure area that draws winds from the North Pacific High through the Golden Gate, which creates the city's characteristic cool winds and fog. The fog is less pronounced in eastern neighborhoods and during the late summer and early fall. As a result, the year's warmest month, on average, is September, and on average, October is warmer than July, especially in daytime.
Because of its sharp topography and maritime influences, San Francisco exhibits a multitude of distinct microclimates. The high hills in the geographic center of the city are responsible for a 20% variance in annual rainfall between different parts of the city. They also protect neighborhoods directly to their east from the foggy and sometimes very cold and windy conditions experienced in the Sunset District; for those who live on the eastern side of the city, San Francisco is sunnier, with an average of 260 clear days, and only 105 cloudy days per year.
Temperatures reach or exceed 80 °F (27 °C) on an average of only 21 and 23 days a year at downtown and San Francisco International Airport (SFO), respectively.[96] The dry period of May to October is mild to warm, with the normal monthly mean temperature peaking in September at 62.7 °F (17.1 °C). The rainy period of November to April is slightly cooler, with the normal monthly mean temperature reaching its lowest in January at 51.3 °F (10.7 °C). On average, there are 73 rainy days a year, and annual precipitation averages 23.65 inches (601 mm). Variation in precipitation from year to year is high. Above average rain years are often associated with warm El Niño conditions in the Pacific while dry years often occur in cold water La Niña periods. In 2013 (a "La Niña" year), a record low 5.59 in (142 mm) of rainfall was recorded at downtown San Francisco, where records have been kept since 1849. Snowfall in the city is very rare, with only 10 measurable accumulations recorded since 1852, most recently in 1976 when up to 5 inches (130 mm) fell on Twin Peaks.
Demonym
Economy
Geography
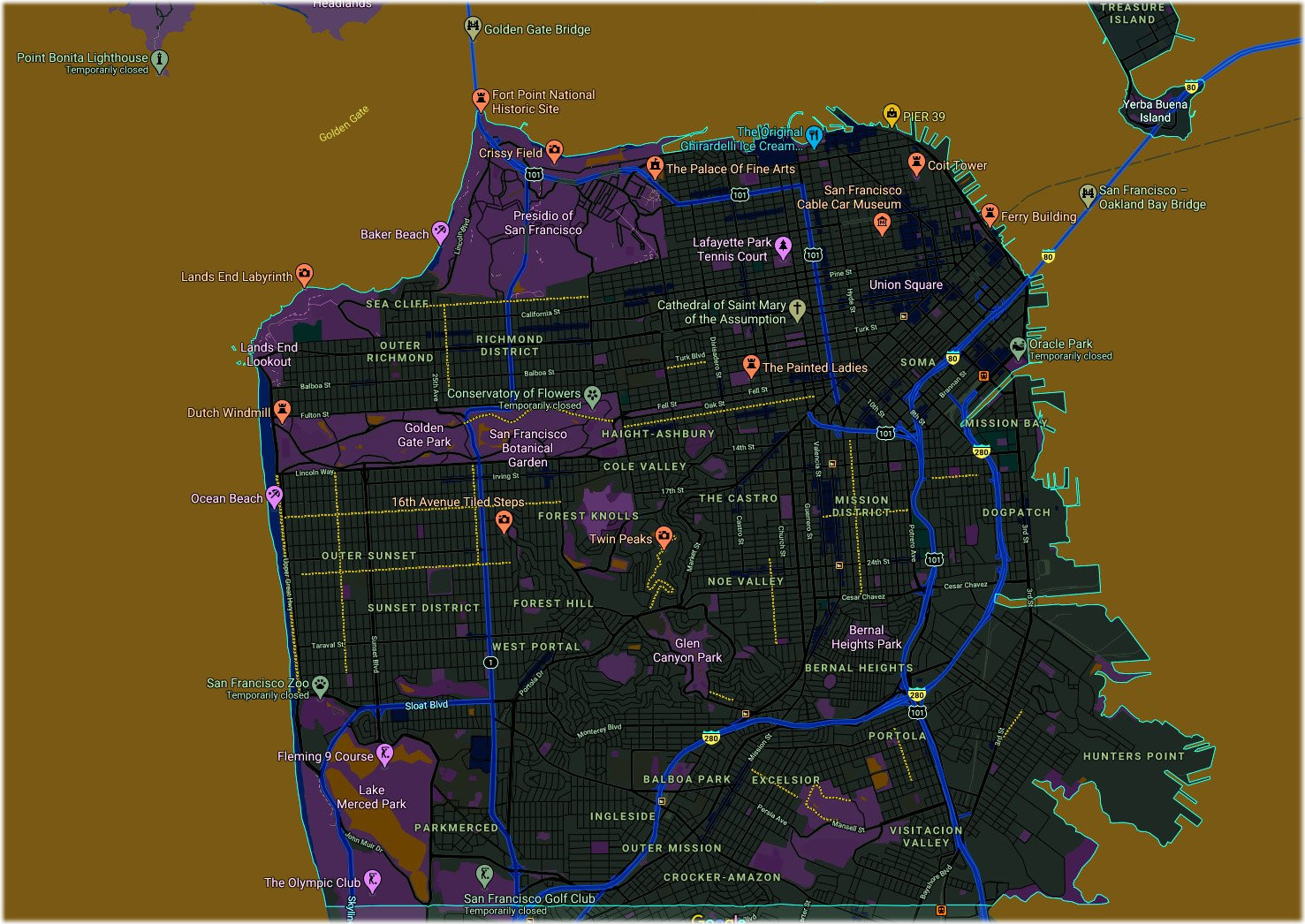
Whoever after due and proper warning shall be heard to utter the abominable word "Frisco",
which has no linguistic or other warrant, shall be deemed guilty of High Misdemeanour, and
shall pay into the Imperial Treasury as penalty the sum of twenty-five dollars. -- Emperor Norton
San Francisco is located on the West Coast of the United States at the north end of the San Francisco Peninsula and includes significant stretches of the Pacific Ocean and San Francisco Bay within its boundaries. Several picturesque islands—Alcatraz, Treasure Island and the adjacent Yerba Buena Island, and small portions of Alameda Island, Red Rock Island, and Angel Island—are part of the city. Also included are the uninhabited Farallon Islands, 27 miles (43 km) offshore in the Pacific Ocean. The mainland within the city limits roughly forms a "seven-by-seven-mile square", a common local colloquialism referring to the city's shape, though its total area, including water, is nearly 232 square miles (600 km2).
There are more than 50 hills within the city limits. Some neighborhoods are named after the hill on which they are situated, including Nob Hill, Potrero Hill, and Russian Hill. Near the geographic center of the city, southwest of the downtown area, are a series of less densely populated hills. Twin Peaks, a pair of hills forming one of the city's highest points, forms an overlook spot. San Francisco's tallest hill, Mount Davidson, is 928 feet (283 m) high and is capped with a 103-foot (31 m) tall cross built in 1934. Dominating this area is Sutro Tower, a large red and white radio and television transmission tower.
The nearby San Andreas and Hayward Faults are responsible for much earthquake activity, although neither physically passes through the city itself. The San Andreas Fault caused the earthquakes in 1906 and 1989. Minor earthquakes occur on a regular basis. The threat of major earthquakes plays a large role in the city's infrastructure development. The city constructed an auxiliary water supply system and has repeatedly upgraded its building codes, requiring retrofits for older buildings and higher engineering standards for new construction. However, there are still thousands of smaller buildings that remain vulnerable to quake damage. USGS has released the California earthquake forecast which models earthquake occurrence in California.
San Francisco's shoreline has grown beyond its natural limits. Entire neighborhoods such as the Marina, Mission Bay, and Hunters Point, as well as large sections of the Embarcadero, sit on areas of landfill. Treasure Island was constructed from material dredged from the bay as well as material resulting from the excavation of the Yerba Buena Tunnel through Yerba Buena Island during the construction of the Bay Bridge. Such land tends to be unstable during earthquakes. The resulting soil liquefaction causes extensive damage to property built upon it, as was evidenced in the Marina district during the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake. Most of the city's natural watercourses, such as Islais Creek and Mission Creek, have been culverted and built over, although the Public Utilities Commission is studying proposals to daylight or restore some creeks.
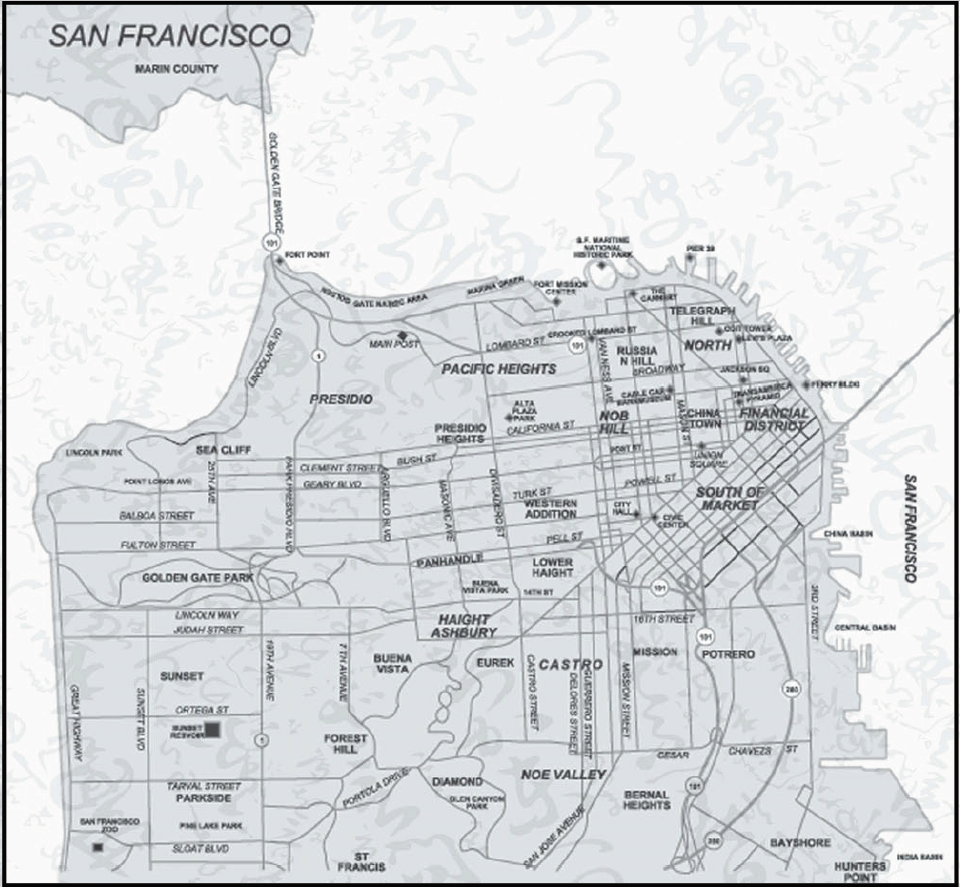
Neighborhoods
The historic center of San Francisco is the northeast quadrant of the city anchored by Market Street and the waterfront. It is here that the Financial District is centered, with Union Square, the principal shopping and hotel district, and the Tenderloin nearby. Cable cars carry riders up steep inclines to the summit of Nob Hill, once the home of the city's business tycoons, and down to the waterfront tourist attractions of Fisherman's Wharf, and Pier 39, where many restaurants feature Dungeness crab from a still-active fishing industry. Also in this quadrant are Russian Hill, a residential neighborhood with the famously crooked Lombard Street; North Beach, the city's Little Italy and the former center of the Beat Generation; and Telegraph Hill, which features Coit Tower. Abutting Russian Hill and North Beach is San Francisco's Chinatown, the oldest Chinatown in North America.[88][89][90][91] The South of Market, which was once San Francisco's industrial core, has seen significant redevelopment following the construction of Oracle Park and an infusion of startup companies. New skyscrapers, live-work lofts, and condominiums dot the area. Further development is taking place just to the south in Mission Bay area, a former railroad yard, which now has a second campus of the University of California, San Francisco and Chase Center, which opened in 2019 as the new home of the Golden State Warriors.
West of downtown, across Van Ness Avenue, lies the large Western Addition neighborhood, which became established with a large African American population after World War II. The Western Addition is usually divided into smaller neighborhoods including Hayes Valley, the Fillmore, and Japantown, which was once the largest Japantown in North America but suffered when its Japanese American residents were forcibly removed and interned during World War II. The Western Addition survived the 1906 earthquake with its Victorians largely intact, including the famous "Painted Ladies", standing alongside Alamo Square. To the south, near the geographic center of the city is Haight-Ashbury, famously associated with 1960s hippie culture. The Haight is now home to some expensive boutiques and a few controversial chain stores, although it still retains some bohemian character.
North of the Western Addition is Pacific Heights, an affluent neighborhood that features the homes built by wealthy San Franciscans in the wake of the 1906 earthquake. Directly north of Pacific Heights facing the waterfront is the Marina, a neighborhood popular with young professionals that was largely built on reclaimed land from the Bay.
In the south-east quadrant of the city is the Mission District—populated in the 19th century by Californios and working-class immigrants from Germany, Ireland, Italy, and Scandinavia. In the 1910s, a wave of Central American immigrants settled in the Mission and, in the 1950s, immigrants from Mexico began to predominate. In recent years, gentrification has changed the demographics of parts of the Mission from Latino, to twenty-something professionals. Noe Valley to the southwest and Bernal Heights to the south are both increasingly popular among young families with children. East of the Mission is the Potrero Hill neighborhood, a mostly residential neighborhood that features sweeping views of downtown San Francisco. West of the Mission, the area historically known as Eureka Valley, now popularly called the Castro, was once a working-class Scandinavian and Irish area. It has become North America's first gay village, and is now the center of gay life in the city. Located near the city's southern border, the Excelsior District is one of the most ethnically diverse neighborhoods in San Francisco. The predominantly African American Bayview-Hunters Point in the far southeast corner of the city is one of the poorest neighborhoods and suffers from a high rate of crime, though the area has been the focus of several revitalizing and controversial urban renewal projects.
The construction of the Twin Peaks Tunnel in 1918 connected southwest neighborhoods to downtown via streetcar, hastening the development of West Portal, and nearby affluent Forest Hill and St. Francis Wood. Further west, stretching all the way to the Pacific Ocean and north to Golden Gate Park lies the vast Sunset District, a large middle class area with a predominantly Asian population.[98] The northwestern quadrant of the city contains the Richmond, also a mostly middle-class neighborhood north of Golden Gate Park, home to immigrants from other parts of Asia as well as many Russian and Ukrainian immigrants. Together, these areas are known as The Avenues. These two districts are each sometimes further divided into two regions: the Outer Richmond and Outer Sunset can refer to the more western portions of their respective district and the Inner Richmond and Inner Sunset can refer to the more eastern portions.
Many piers remained derelict for years until the demolition of the Embarcadero Freeway reopened the downtown waterfront, allowing for redevelopment. The centerpiece of the port, the Ferry Building, while still receiving commuter ferry traffic, has been restored and redeveloped as a gourmet marketplace.
Districts
Richmond
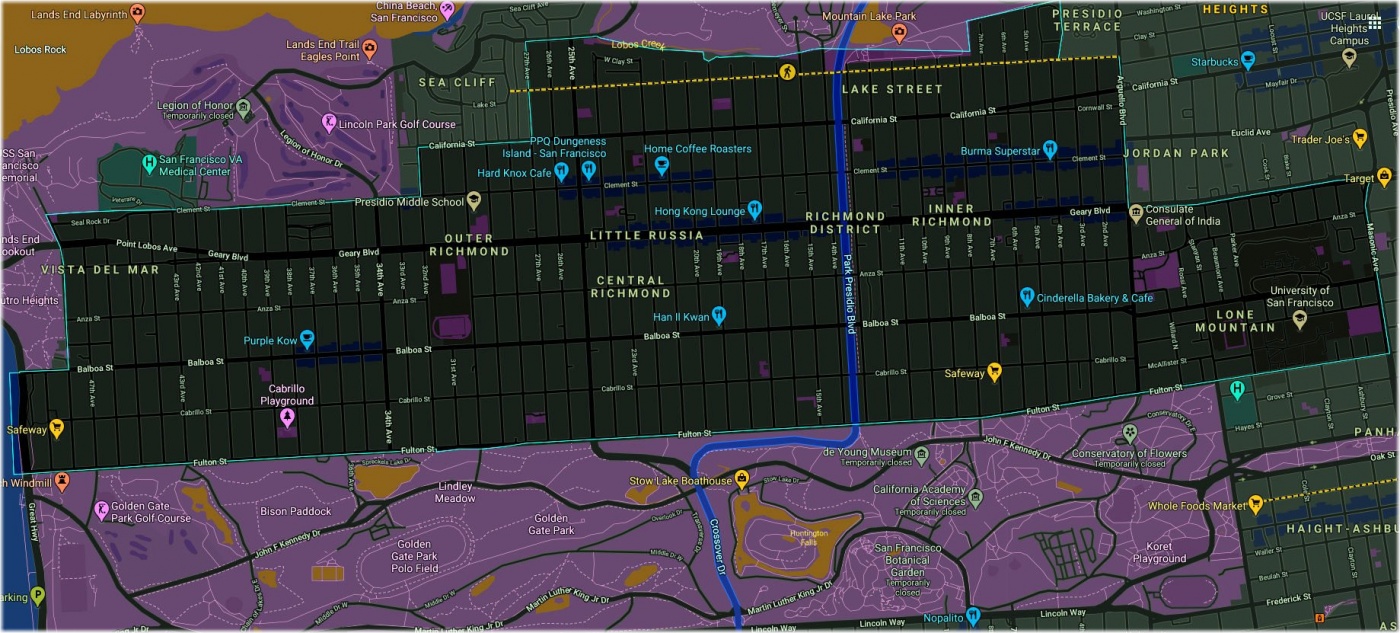
The Richmond District is a neighborhood in the northwest corner of San Francisco, California, developed initially in the late 19th century. It is sometimes confused with the city of Richmond, which is 20 miles (32 km) northeast of San Francisco.
The Richmond is in many ways defined by its relation to the parks; bordered by Golden Gate Park on the south, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and Lincoln Park, Land's End, Mountain Lake Park and the Presidio of San Francisco to the north, bisected by the Presidio Greenbelt.
The Richmond has many influences from the Chinese-American culture. One of its three commercial strips, Clement Street in the inner Richmond segment is sometimes called the second Chinatown due to the high concentration of Chinese establishments.
The other two commercial strips are Geary Boulevard and Balboa Street.
The Richmond also has deep Irish and Russian roots and has many Catholic and Orthodox churches.
Sub-districts
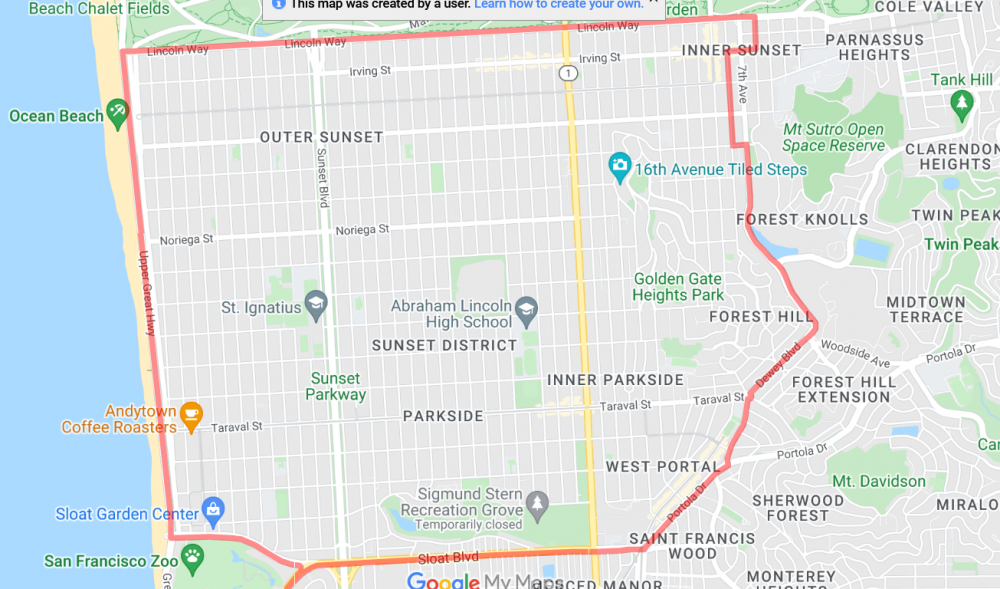
Sunset
Location
The Sunset District is the largest neighborhood within the city and county of San Francisco. Golden Gate Park forms the neighborhood's northern border, and the Pacific Ocean (or, more specifically, the long, flat strand of beach known as Ocean Beach) forms its western border. A section of the Sunset District towards its southeastern end is known as the Parkside neighborhood. Prior to the residential and commercial development of the Sunset District, much of the area was covered by sand dunes and was originally referred to by 19th century San Franciscans as the "Outside Lands."
The Sunset District and the neighboring Richmond District (on the north side of Golden Gate Park) are often collectively known as The Avenues, because the majority of both neighborhoods are spanned by numbered north-south avenues. When the city was originally laid out, the avenues were numbered from 1st to 49th, and the east-west streets were lettered A to X. In 1909, to reduce confusion for mail carriers, the east-west streets and 1st Avenue and 49th Avenue were renamed. The east-west streets were named in ascending alphabetical order in a southward direction after prominent 19th-century American politicians, military leaders, or explorers; 19th-century Mexican landowners; and Spanish conquistadors. 1st Avenue was renamed Arguello Boulevard, and 49th Avenue was renamed La Playa Street (Spanish for "the beach").
Today, the first numbered avenue is 2nd Avenue, starting one block west of Arguello Boulevard, and the last is 48th Avenue near Ocean Beach. The avenue numbers increase incrementally, with one exception: what would be 13th Avenue is known as Funston Avenue, named after Frederick Funston, a U.S. Army general known for his exploits during the Spanish–American War and Philippine–American War, and for directing the U.S. Army response to the 1906 San Francisco earthquake.
The east-west streets in the Sunset appear mostly in alphabetical order. These streets are: Lincoln Way (bordering the south side of Golden Gate Park), Hugo (from Arguello to 7th Avenue only), Irving, Judah, Kirkham, Lawton, Moraga, Noriega, Ortega, Pacheco, Quintara, Rivera, Santiago, Taraval, Ulloa, Vicente, Wawona, Yorba, and Sloat Boulevard. "X" was originally proposed to be Xavier, but was changed to Yorba due to a pronunciation controversy.
History
The origin of the "Sunset" name is not entirely clear. One claim indicates that Aurelius Buckingham, a developer who owned property in the area, coined the term in 1886. Another claim comes from the California Midwinter Exposition, held in Golden Gate Park in 1894 and also known as "The Sunset City."
Before construction of the Twin Peaks Tunnel in 1917, the Sunset was a vast, sparsely inhabited area of large sand dunes and coastal scrub land known as the "Outside Lands." Development was initiated in the 1870s and 1880s with construction of Golden Gate Park, but it did not reach a full scale until after the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, when small lots of tract homes and row homes now characteristic of the neighborhood were built into the sand dunes. These tract homes would displace a smaller original settlement built into the dunes called Carville, which was so named for squatters that lived in abandoned horsecars (horse-drawn trolleys) and cable cars that were dumped in the sand dunes. Development increased by the 1930s, as the Sunset was built and developed into a streetcar suburb. The post–World War II baby boom in the 1950s saw the last of the sand dunes leveled down and replaced with more single- and multifamily homes. In these developments, built mostly by Henry Doelger, entire blocks consist mainly of houses of the same general character, differentiated by variations in their stucco facades and mirrored floorplans, with most built upon 25-foot-wide (7.6 m) lots with no free space between houses. Later, Oliver Rousseau built more individualistic homes in the district.
Historically, the Sunset has been an Irish and Italian ethnic enclave. Beginning in the late 1960s the neighborhood saw a steady influx of Asian (mostly Chinese) immigrants following the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965 which lifted racial quotas allowing for more non-European nationals to immigrate to the United States. Additionally, the Handover of Hong Kong motivated many Chinese to immigrate to the U.S. due to the political and economic uncertainties. In 1999, around 60% of the homeowners in the Sunset and Richmond districts were Chinese.
Sub-Districts
Inner Sunset
The Inner Sunset is bordered by Lincoln Way to the north, 2nd Ave to the east, Quintara Street to the south, and 19th Avenue to the west. This far-east section of the Sunset is located just west of Mount Sutro. The main commercial area is along Irving Street from 5th Avenue to 12th Avenue, and along 9th Avenue from Lincoln Way to Judah Street, much of which is dotted with a variety of restaurants and shops.
The Inner Sunset hosts a variety of local businesses, including restaurants, bars, breweries, book stores, bakeries, coffee shops, ice cream parlors, clothes and shoe stores, a tattoo parlor, and a wine bar. Many of these establishments are clustered around the intersection of 9th Avenue and Irving Street. Food offered by the restaurants located in the Inner Sunset includes pizza, Mexican, Thai, Persian, Korean, Malaysian, Hawaiian, Greek, Ethiopian, Pakistani, Cajun/Creole, Dim Sum, Turkish, Peruvian, Chinese, Vietnamese, California Cuisine, Mediterranean, Indian, Japanese, Vegetarian.
The Inner Sunset is the 12th wealthiest neighborhood in San Francisco with a median income of $112,050. [10] The median sale price of homes in the Sunset District is $1.5M.
Central Sunset
The Central Sunset is bounded by Lincoln Way to the north, 19th Avenue to the east, Quintara Street to the south, and Sunset Boulevard to the west. This area is mostly residential with cookie-cutter homes and large lots and a commercial strip along Irving Street from 19th Avenue to 24th Avenue and on Noriega Street from 19th Avenue to 27th Avenue and 30th Avenue to 33rd Avenue. Features of the area include the Sunset Reservoir (which takes up eight square blocks between Ortega and Quintara streets and 24th and 28th avenues), which has a small park surrounding its outer rim; Golden Gate Park; the Sunset Recreation Center; and Abraham Lincoln High School.
Outer Sunset
The Outer Sunset is bordered by Lincoln Way to the north, Sunset Boulevard (between 36th and 37th avenues) to the east, Sloat Boulevard to the south, and Ocean Beach to the west. The primary commercial avenues are Judah, Noriega, and Taraval. The Outer Sunset is the foggiest section in San Francisco due to its close proximity to Ocean Beach. The area's main attractions include the San Francisco Zoo, Golden Gate Park, Ocean Beach, and Lake Merced.
Attractions
The western part of the Sunset borders the cold northern California Pacific Ocean coastline, so it tends to get much of the fog San Francisco is famous for. The Sunset can be foggy and chilly for some days during summer. The Sunset's finest weather is usually from August through December, when regional air patterns transition from onshore to offshore weather and the area is free of fog. Sand carried by Pacific Ocean winds can be found on roadways and driveways within the first five to ten blocks east of Ocean Beach.
The Sunset District contains several large park and recreation areas. The San Francisco Zoo is located in the southwestern corner of the neighborhood by Lake Merced, the largest lake within San Francisco. Also within the Lake Merced area are several golf courses: the private Olympic Club and San Francisco Golf Club, and the public TPC Harding Park. Across from Lake Merced is Fort Funston, an old coastal battery, now part of the Golden Gate National Recreation Area. Fort Funston notably has some of the last remnants of the sand dune ecosystem that once covered the entire Sunset District.
There is a year-round, Sunday morning farmers' market which is located at 1315 8th Avenue (the parking lot between 8th and 9th Avenues). The market is operated by the Pacific Coast Farmers' Market Association and is sponsored by the Inner Sunset Park Neighbors. The Inner Sunset Farmers' Market offers California-grown produce, fish, eggs, and meat, as well as local food vendors and artisans.
Stern Grove, a heavily wooded park and amphitheater located on Sloat Boulevard between 19th and 34th avenues, is known for its annual summer festival.
Three parks lie on the far east border of the district: the northernmost is Grand View Park (also referred to as Turtle Hill) a small, elevated park surrounded by 14th and 15th Avenues, as well as Noriega Street; moving south, next is Golden Gate Heights Park, just east of 14th Avenue north of Quintara; and Hawk Hill Park, also east of 14th Avenue at Santiago. These natural areas belong to a remnant ridge-top system and include some of the last-remaining sand-dune communities in the city.
Education
The San Francisco Unified School District operates public K–12 schools.
Educational institutions include the Parnassus campus and medical center of the University of California, San Francisco, located in Inner Sunset; the main campus of San Francisco State University, located in the southwestern corner of the neighborhood across from Lake Merced; Abraham Lincoln High School, located in the center of the Sunset District; St. Ignatius College Preparatory (a private, coeducational school operating in San Francisco since 1855) located since 1969 adjacent to Sunset Boulevard; and Lowell High School, the oldest public high school west of the Mississippi and one of the top performing ones in the United States.
Beach Culture
The strip near the Pacific Ocean has a notable population of surfers who take advantage of the sometimes excellent surf conditions of Ocean Beach. Because of the cold Pacific current that brings ocean water from Alaska, it is usually necessary to wear a wet-suit when surfing at Ocean Beach. Several surf shops can be found near the beach in the Outer Sunset.
Several playgrounds are located in the Sunset, including Sunset Playground and Recreation Center, Blue Boat Playground, West Sunset, McCoppin Square, and South Sunset.
Climate
Like much of the coast of Northern California, Sunset district has a cool summer Mediterranean climate, albeit with an unusual annual temperature distribution. The warmest days of the year occur in October and then the coldest nights of the year occur just two months later in December. Its climate is strongly influenced by the Pacific Ocean and therefore has even cooler summers and milder winters than downtown San Francisco. Rainfall follows a seasonal pattern with plentiful precipitation in the winter (almost all of this falling as rain) and extremely dry albeit foggy summers.
Lakeshore
Tenderloin
Introduction
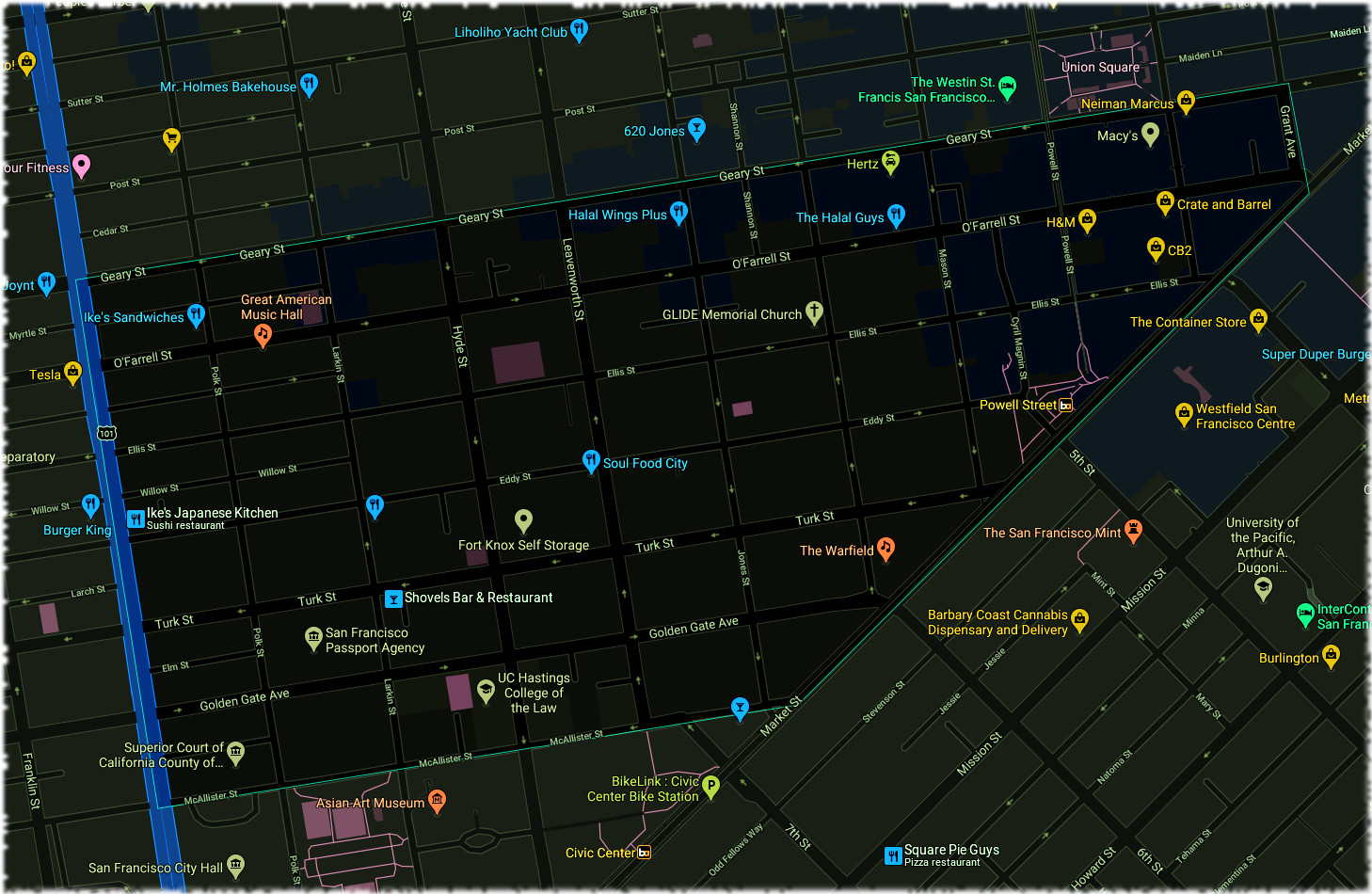
The Tenderloin is a neighborhood in downtown San Francisco, in the flatlands on the southern slope of Nob Hill, situated between the Union Square shopping district to the northeast and the Civic Center office district to the southwest. It encompasses about 50 square blocks, and is a large wedge/triangle in shape (point faces East). It is historically bounded on the north by Geary Street, on the east by Mason Street, on the south by Market Street and on the west by Van Ness Avenue. The northern boundary with Lower Nob Hill historically has been set at Geary Street.
The terms "Tenderloin Heights" and "The Tendernob" refer to the area around the indefinite boundary between the Upper Tenderloin and Lower Nob Hill. The eastern extent, near Union Square, overlaps with the Theater District.
Part of the western extent of the Tenderloin, Larkin and Hyde Streets between Turk and O'Farrell, was officially named "Little Saigon" by the City of San Francisco.
History
The Tenderloin took its name from an older neighborhood in New York with similar characteristics. There are several explanations of how that neighborhood was named. Some said it was a reference to the neighborhood as the "soft underbelly" (analogous to the cut of meat) of the city, with allusions to vice and corruption, especially graft. Another popular explanation, probably folklore, attributes the name to a New York City police captain, Alexander S. Williams, who was overheard saying that when he was assigned to another part of the city, he could only afford to eat chuck steak on the salary he was earning, but after he was transferred to this neighborhood he was making so much money on the side soliciting bribes that now he could eat tenderloin instead. Another version of that story says that the officers who worked in the Tenderloin received a "hazard pay" bonus for working in such a violent area, and thus were able to afford the good cut of meat. Yet another story, also likely apocryphal, is that the name is a reference to the "loins" of prostitutes.
The Tenderloin borders the Mission/Market Street corridor, which follows the Spaniards' El Camino Real, which in turn traced an ancient north–south Indian trail. The Tenderloin is sheltered by Nob Hill, and far enough from the bay to be on solid ground. There is evidence that a community resided here several thousand years ago. In the 1960s, the area was excavated to develop the BART/MUNI subway station at Civic Center.
The Tenderloin has been a downtown residential community since shortly after the California Gold Rush in 1849. However, the name "Tenderloin" does not appear on any maps of San Francisco prior to the 1930s; before then, it was labeled as "Downtown", although it was informally referred to as "the Tenderloin" as early as the 1890s. The area had an active nightlife in the late 19th century with many theaters, restaurants and hotels. Notorious madam Tessie Wall opened her first brothel on O'Farrell Street in 1898. Almost all of the buildings in the neighborhood were destroyed by the 1906 earthquake and the backfires that were set by firefighters to contain the devastation. The area was immediately rebuilt with some hotels opening by 1907 and apartment buildings shortly thereafter, including the historic Cadillac Hotel. By the 1920s, the neighborhood was notorious for its gambling, billiard halls, boxing gyms, "speakeasies", theaters, restaurants and other nightlife depicted in the hard boiled detective fiction of Dashiell Hammett, who lived at 891 Post Street, the apartment he gave to Sam Spade in The Maltese Falcon. Also around this time, due to Red Light Abatement Act, prostitution and other vice began to be pushed out from the Barbary Coast district to the more southern and less business-occupied Tenderloin.
In the mid-20th century, the Tenderloin provided work for many musicians in the neighborhood's theaters, hotels, burlesque houses, bars and clubs and was the location of the Musician's Union Building on Jones Street. The most famous jazz club was the Black Hawk at Hyde and Turk Streets where Dave Brubeck, Miles Davis, Thelonious Monk, Gerry Mulligan, and other jazz greats recorded live albums for Fantasy Records in the late 1950s and early 1960s.
With housing consisting almost entirely of single-room-occupancy hotel rooms, studio and one bedroom apartments, the Tenderloin historically housed single adults and couples. After World War II, with the decline in central cities throughout the United States, the Tenderloin lost population, creating a large amount of vacant housing units by the mid-1970s. Beginning in the late 1970s, after the Vietnam War, the Tenderloin received large numbers of refugees from Southeast Asia—first ethnic Chinese from Vietnam, then Khmer from Cambodia and Hmong from Laos. The low-cost vacant housing, and the proximity to Chinatown through the Stockton Street Tunnel, made the area appealing to refugees and resettlement agencies. Studio apartments became home for families of four and five people and became what a local police officer called "vertical villages." The Tenderloin quickly increased from having just a few children to having over 3,500 and this population has remained. A number of neighborhood Southeast Asian restaurants, bánh mì coffee shops, ethnic grocery stores, video shops, and other stores opened at this time, which still exist.
The Tenderloin has a long history as a center of alternate sexualities, including several historic confrontations with police. The legendary female impersonator Ray Bourbon, a performer during the Pansy Craze, was arrested in 1933 while his show "Boys Will Be Girls" was being broadcast live on the radio from Tait's Cafe at 44 Ellis Street. In the evening of August 13, 1961, 103 gay and lesbian patrons were raided in the Tay-Bush Inn, a café frequently visited by gay and lesbian patrons.[14] As a response to police harassment, S.F. bar owners formed the San Francisco Tavern Guild. A study into prostitution in the Tenderloin found that while trans women face discrimination from certain professions and their sexual partners, sex workers in the Tenderloin area were adept at overcoming some such difficulties.
On New Year's Day in 1965, police raided a Mardi Gras Ball at California Hall[17] on Polk Street sponsored by the Council on Religion and the Homosexual, lining up and photographing 600 participants and arresting several prominent citizens. One of the first "gay riots", pre-dating the Stonewall riots in New York, happened at Compton's Cafeteria[18] at Turk and Taylor Streets in August 1966 when the police, attempting to arrest a drag queen, sparked a riot that spilled into the streets. The group ended up smashing the windows of the police car and burned a nearby newspaper stand to the ground; the riot promoted the formation of the Gay Activists Alliance.[19] Prior to the emergence of The Castro as a major gay village, the center of the Tenderloin at Turk and Taylor and the Polk Gulch at the western side of the Tenderloin were two of the city's first gay neighborhoods and a few of these historic gay bars and clubs still exist.
The apartment where Dashiell Hammett wrote The Maltese Falcon was once in the boundaries of the Tenderloin at the corner of Hyde and Post. Both the movie and book were based in San Francisco's Tenderloin. There is also an alley in what is now Nob Hill, named for the book's author (Dashiell Hammett). It lies outside the Tenderloin because the boundary was defined with borders different from today's. Some locations, such as Sam Spade's apartment and John's Grill, also no longer lie in the Tenderloin because local economics and real estate have changed the character and labeling of areas over time.
In July 2008, the area was designated as a historic district on the National Register of Historic Places.
In 2017, a portion was declared the Compton's Transgender Cultural District commemorating the historic transgender population and culture and in particular, the 1966 transgender and queer uprising, the Compton's Cafeteria riot.
Attractions and Characteristics
Nestled near the downtown area, the Tenderloin has historically resisted gentrification, maintaining a seedy character and reputation for crime. Squalid conditions, homelessness, crime, illegal drug trade, prostitution, liquor stores, and strip clubs give the neighborhood a seedy reputation.
Part of the neighborhood forms part of the theater district. Prominent theatres include the Geary, the home of the American Conservatory Theater,[23] and the Curran, Golden Gate and Orpheum Theatres operated by the Shorenstein Nederlander Organization. Alternative theaters in the Tenderloin include EXIT Theatre, which operates four storefront theaters and produces the San Francisco Fringe Festival, the New Conservatory Theater, the Phoenix Theater, CounterPulse, PianoFight, the New Music Center and others. Alternate galleries include The Luggage Store, the 509 Cultural Center, and others. The neighborhood had many bars dating to prohibition and before with dive bars, including some left over from when the neighborhood housed large numbers of merchant seamen but most of those have closed or been transformed. One bar is built on the site of a previous speakeasy, Bourbon and Branch, at the corner of Jones and O'Farrell Streets. The original speakeasy was restored in the bar's basement, including many of the original decorations. Many bars have entertainment including the historic drag bar Aunt Charlie's. Larger live music venues include the Great American Music Hall and the Warfield Theatre. Historically, the Tenderloin has had a number of strip clubs, although their number has decreased in recent decades. The best known is the Mitchell Brothers O'Farrell Theatre. The Tenderloin is also a hub for the gender diverse community. The categories of LGBTIQ created a new gender politics that helped to distinguish between the different groups; the Tenderloin was heavily populated by the transgender community. Many street activists paved the way for change, such as Anne Ogborn.
In his seminar 'Take Charge of Your Life', Jim Rohn recounted his visits to the Tenderloin to experience the "human tragedy". He described his visit to a bar in the Tenderloin where the bar tender told him about a dancer by the name of Cookie, who was severely crippled and had a child suffering from leukemia.
Gentrification
The position held by policy-makers regarding gentrification is often divided, with one side of the debate arguing that it is of benefit to the public economy and revitalisation of the built setting, whilst the other side argues that the huge social costs and displacement of people, especially the poor, outweigh all potential strengths of the process.
Murals
The Tenderloin serves as a mecca for the art scene in San Francisco, housing the "White Walls" gallery and "Shooting Gallery". The Tenderloin has been home to mural work by artists such as Johanna Poethig, Mona Caron, Banksy, Shepard Fairey, Barry McGee, Mike Giant, Blek Le Rat and Dan Plasma.
The "Book & Job" gallery has become known for hosting skating legends such as Tommy Guerrero and promoting "Zine Weekends."
Crime
The Tenderloin is a high-crime neighborhood, particularly violent street crime such as robbery and aggravated assault. Seven of the top 10 violent crime plots (out of 665 in the entire city as measured by the San Francisco Police Department) are adjacent plots in the Tenderloin and Sixth and Market area. The neighborhood was considered to be the origin of a notorious Bahala Na Gang (BNG) imported from the Philippines. In the late 1960s to the mid-1970s, the gang was involved in extortion, drug sales, and murder for hire.
Graffiti art and tagging are a common problem in the neighborhood. Dealing and use of illicit drugs occurs on the streets. Property crimes are common, especially theft from parked vehicles. Violent acts occur more often here and are generally related to drugs. The area has been the scene of escalating drug violence in 2007, including brazen daylight shootings, as local gangs from San Francisco, and others from around the Bay Area battle for turf. 14 of the city's 98 homicides took place in the area in 2007.
The first block of Turk Street, between Taylor and Mason, had one of the highest rates of violence and drug activity in San Francisco, according to a survey conducted by the Tenderloin Housing Clinic. On January 31, 2014, parking was banned on both sides of the street in an effort to reduce violence and drug activity. Without parked cars to hide illegal activity, there were fewer loiterers, and a decrease in drug activity.
Additionally, on April 10, 1984, notorious serial killer Richard Ramirez committed his first known murder in a hotel basement, where he was living, in the Tenderloin district.
Social Issues
High prevalence of sex work in the Tenderloin area has been associated with a high rate of sexually transmitted infections, including HIV, especially among men who have sex with other men and those who also inject drugs. Contributing factors include a lack of sex education and safe sex practices, including condom use. In a 2000 survey, 59% of men who performed sex with other men did not report condom use, with higher rates of unsafe sex practices among those who are not engaged in paid sex work.
Social Services
The Tenderloin has been the home of Raphael House, the first provider in the city of shelter for homeless parents and children, since 1971. It is an ethnically diverse community, consisting of families, young people living in cheap apartments, downtown bohemian artists, and recent immigrants from Latin America and Southeast Asia. It is home to a large population of homeless, those living in extreme poverty, and numerous non-profit social service agencies, soup kitchens, religious rescue missions, homeless shelters and single room occupancy hotels. Many homeless youths in the Tenderloin district are at risk of serious emotional and psychological problems arising from past traumatic experiences. Lack of appropriately targeted options available in the area has meant many youths will have few viable paths to deal effectively with their problems.
The Tenderloin Housing Clinic has offered important social services to the poor of this neighborhood for decades. The Care Through Touch Institute, located between Hyde and Leavenworth Streets, offers free seated massage therapy to clients in the Tenderloin community. The founder and director of CTI, Mary Ann Finch, began offering services here in 1997, after being inspired by her volunteer work with Mother Teresa in India.
Religious institutions providing community services to the Tenderloin include Glide Memorial Church, which was reinvigorated by Cecil Williams in 1963, St. Anthony's, a program of the Franciscans and San Francisco City Impact founded in 1984 by Pastor Roger Huang. San Francisco City Impact's K-8 private school, the San Francisco City Academy, was the first K-8 school in the Tenderloin District; founded in 1997. These all provide meals and other social services to poor and homeless residents and others. Glide and the surrounding neighborhood provided much of the setting for the 2006 film The Pursuit of Happyness. In 2008, The Salvation Army opened the Ray and Joan Kroc Community Center, a multipurpose center featuring a gym, swimming pool and fitness center among other amenities. The funding for this center was made possible by a $1.5 billion bequest from Joan Kroc, the widow of McDonald's founder, Ray Kroc. Adjacent to the Kroc center is Railton Place, a 110-unit apartment complex run by the Salvation Army for former foster youth, homeless veterans, and adults recovering from addictions. In 2016, the Tenderloin Community Benefit District (TLCBD) announced the implementation of a new public-private initiative, Operation Leadership, which aims to help strengthen existing street cleaning and beautification services.
As transgender women often face barriers such as discrimination and stigma when accessing health care, and show reluctance to disclose their gender when seeking health related services, a collaborative project named 'TRANS' was set up near the Tenderloin to appropriately address the multifaceted needs of this diverse population, as well as offering support.
In their study, Sausa, Keatley, Operario (2007) concluded that sex work for transgender women of colour must be viewed as a forced consequence of structural barriers that they face, as well as an informed choice for survival as a result of these barriers.
The Tenderloin Senior Organizing Project (TSOP; formerly known as the Tenderloin Senior Outreach Project) was initiated when local university staff realized that many seniors felt afraid of crime, rent increases, and inadequate income. They facilitate interpersonal communication through coffee & refreshments, and groups of elderly people were encouraged to meet each other.
Larkin Street Youth Services is a non-profit organization that offers a continuum of services that inspires youth to move beyond the street. Services run the gamut from street outreach and temporary shelters to transitional living programs, health and wellness services, and comprehensive education and employment programs.
Culture
In recent years, residents have spearheaded a local arts revival.
In 1987, residents and others from the Aarti Hotel on Leavenworth Street founded the 509 Cultural Center at 509 Ellis Street. After the 1989 earthquake damaged that facility, artists founded The Luggage Store at 1007 Market, at the intersection of 6th Street, Market, Taylor and Golden Gate Avenue. In 1989 the Tenderloin Reflection and Education Center (TREC) spun off from St Anthony foundation and operated a cultural center including dance, music, writing quilting, and other arts workshops in the St. Boniface Neighborhood Center. Artists and activists such as Eric Ehn from the Iowa Writing Workshop and Theatre Artaud; Miya Masoaka, a recording artist with Asian Improv Records; Lucy Jane Bledsoe, published novelist and writer for the East Bay Express; Pearl Ubungen, choreographer; Ben Clarke, Founding Editor of Freedom Voices; and Maketa Groves, poet and published author at Curbstone Press; and Tenderloin resident and Athabaskan poet Mary TallMountain offered numerous free workshops. TREC and its publishing project Freedom Voices continue to offer workshops on an occasional basis at the Public Library, Hospitality House, the Faithful Fools and other locations in the neighborhood. Tender Leaves, the Center's literary journal was published from 1987 to 2006.
From 2006 to 2009, The Loin's Mouth – conceived by its editor Rachel M. – was a semi-quarterly publication about life in the Tenderloin and Tendernob areas. Since then, others have come about to fill the gap including the Tenderloin Reading Series, which is a quarterly literary event in the neighborhood as well as The Tender, a local journal focusing on the events, food, and politics of the neighborhood.
In 2006, Gray Area Foundation for the Arts was formed to produce, exhibit, and develop creativity with the most contemporary new media technologies. Initially located on Taylor Street in an 8,000 sq ft (740 m2) space, they have since moved across the street to rent space from The Warfield.
In years past, the local Vietnamese Community has hosted the Tết celebration of the Vietnamese Lunar New Year in the Little Saigon section of the Tenderloin.
Parks and Recreation
Historically, the downtown Tenderloin had no parks between Union Square to the East and Civic Center Plaza to the West until a number of activists, who organized the City's Citizens Committee for Open Space, advocated for more open space in the Tenderloin in the 1970s. As a result, a number of parks and playgrounds were created including first Boeddeker Park, a multi-use facility, then the youth-oriented Tenderloin Playground, followed by a number of mini-playgrounds.
Boeddeker Park, located at the corner of Eddy and Jones Streets, is one of the most used parks per square foot in the City. It underwent a renovation, completed in December 2014, which has revitalized the park. YMCA and the Boys and Girls Club occupy the clubhouse, providing programming for youth and seniors. "It's the hub of positive community togetherness", Tenderloin police Capt. Jason Cherniss said of the park. "It's not necessarily police, it's community. It's ripe for that now. We're all getting more connected and sharing information."
The Tenderloin Children's Playground, on Ellis Street between Leavenworth and Hyde Streets, was opened in 1995 and has attractive indoor and outdoor recreational facilities and hosts a number of community and family events.
Sgt. John Macaulay Park, named after a San Francisco police officer who was killed in the adjacent alley while on duty, is a small gated playground at the corner of O'Farrell and Larkin Streets. Although the park is located across the street from a strip club, it is frequented by parents and children from the neighborhood.
The "Tenderloin National Forest" (a project of the nonprofit organization The Luggage Store/509 Cultural Center) is an unofficial park that was established in 1987 that maintains the park and opening hours. It is located on Cohen Alley just off Ellis Street.
Renaming Attempt
In March 2011, People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA) Vice President Tracy Reiman sent Mayor Ed Lee a letter proposing for renaming of the neighborhood and suggesting an alternative name like the Tempeh District, claiming "the city deserves a neighborhood named after a delicious cruelty-free food instead of the flesh of an abused animal". The proposal was widely met with ridicule by locals and Mayor Lee responded that it was more important to improve the lives of the residents than rename the neighborhood.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tenderloin,_San_Francisco
History
A rich and at times tragic history precedes the current state of affairs in San Francisco, though many of the vampires embroiled in the conflict are unaware of it (and perhaps doomed to repeat it). What both Kindred and Kuei-jin know is that history has picked up its pace in the Bay Area as well as the rest of the world for some time now. It is a pendulum racing on the downward swing , a prisoner of both gravity and momentum and subject to forces and paths not of its choosing. Aware of this, both sides fear there may be no stopping the events they set in motion within the city.
The Earliest Days
While San Francisco’s history only covers a two- century span, the history of the Bay area extends back much farther than that. Native American tribes like the Ohlone and the Miwok inhabited the region long before the arrival of the first Europeans or Asians landed on the shores of North America. These people knew nothing of t he Curse of Caine or the Fall of the Wan Xian, although they understood the creatures haunting the world’s dark and wild places. For the most part, the tribes remained small, warding off undue attention from their preternatural predators. They lived in relative peace with the Changing Folk of the wilds, never dreaming their fellow mortals from across the Atlantic would prove the greatest threat to their existence.
Exploration & Settlement
The first European visitors to curse the shores of California came in 1542, when Portuguese explorer Juan Rodriguez Cabrillo circumnavigated the tip of South America and sailed as far north as the Russian River, mapping the western coast of South and North America along his route. In 1579, famed English sailor Sir Francis Drake landed on California’ s northern coast, pausing briefly to claim the land for Queen Elizabeth before repairing his ships and setting sail once again. Sebastian Cermeno, another Portuguese explorer, “discovered” Punta de los Reyes (King’ s Point) in the 1590s. All the visiting Europeans missed the narrow entrance to San Francisco Bay, however, shrouded as it was by mist and nearly invisible from the sea. It would be centuries more before a European discovered the site of what would become the city of San Francisco.
In 1769, a Spanish soldier named Gaspar de Protola accidentally stumbled upon the bay’s entrance while sailing to Monterey Bay in the south. Six years later, Juan Ayala actually sailed into San Francisco Bay on a mapping expedition for the Spanish crown. It did not take the Spanish long to realize the value of their new discovery, given its strategic and economic potential.
In 1776, about a week before the thirteen English colonies on the other side of the continent declared their independence, Juan Bautista de Anza and some thirty Spanish-speaking families made their way from Sonora, Mexico to San Francisco Bay. They claimed the land for Spain and settled there. Their headquarters was an adobe fort they named the Presidio.
The settlers established a mission about a mile away from the fort. The priests officially named the mission Nuestra Senora de Dolores or Mission Delores, and dedicated the church to St. Francis of Assisi; it was known as “San Francisco,” the name later applied to the bay itself. The mission’ s priests took an interest in the spiritual welfare of the local Indian tribes, ensuring they were baptized and converted to Christianity; for the most part, the natives welcomed trade with the new settlers.
Independence & Growth
In 1821, Mexico won its independence from Spain, secularizing the Spanish missions and abandoning interest in the spiritual well being of the natives — or anyone else, for that matter. Freed from European rule, California’s ports opened for trade and shipped a wealth of goods (mostly hides, furs, wood and tallow) by sea around Cape Horn to the burgeoning factories in New England and New York. Trappers and hunters told tall tales about the strange beasts they encountered in the California hills, but few paid them any heed so long as the goods continued to flow.
The area’s growing prosperity was enough to convince English sailor William Richardson to jump ship in 1822 and settle there. He fell in love with the daughter of the Presidio’ s commandant and converted to Catholicism to marry her. He established a trading post that he named Yerba Buena (or “good herb”) for the wild mint growing in the area. The aptly chosen name later became a source of great humor to the people of San Francisco in the 1960s. Richardson’ s enterprise was wildly successful, and Yerba Buena grew from a trading post to a small town, with a saloon of ill repute frequented by English-speaking hunters and trappers.
Even though Yerba Buena and Mission Dolores grew, their population remained a few hundred at best, comprised of mostly farmers, trappers and a handful of soldiers stationed at the Presidio. During the war between the United States and Mexico in 1847, U.S. Marines from the warship Portsmouth seized the Presidio and the main plaza of Yerba Buena. The dozen or so Mexican soldiers at the Presidio surrendered without firing a single shot. Commander John Montgomery raised the U.S. flag and declared California an American territory. Among the first acts of the new territorial government was to change the settlement’s name to that of the bay: San Francisco.
Such small political victories were certainly of no interest to either the Kindred hunting in the nighttime streets of Boston, New York and Philadelphia, or to those sleeping by day in the mansions of Louisiana, Georgia or Carolina. The events in San Francisco were of even less interest to the Kuei-jin, who barely knew of California at all and remained far more concerned with the Opium Wars brought on by European (and Kindred) incursion into the Middle Kingdom. That, however, was about to change with a single word....
Gum San: The Golden Mountain
“Gold! Gold in the American River!” Mormon preacher Sam Brannan shouted that memorable statement while running through San Francisco’s streets in 1848. Although Brannan was a notorious charlatan, in this case he shouted the truth. Gold was found in the riverbed at a sawmill owned by Swiss-born John Augustus Sutter. Despite Sutter’s best efforts to keep the discovery quiet, the news spread like wildfire. Sam Brannan, incidentally, purchased large tracts of coastal land in San Francisco, as well as cornering the market on shovels, pickaxes and canned goods before making his fateful announcement. He became fabulously wealthy without turning over a single spade of dirt.
It seemed the world was primed for the news from San Francisco. The “Year of Revolutions” swept through Europe, with political and social unrest in many of her major cities. The Potato Famine stalked Ireland, driving people from their homes in hope of a new life elsewhere. The United States caught its breath following the war with Mexico while the conflicts leading to the Civil War simmered beneath the surface. China reeled from the Opium Wars and the abdication of Hong Kong to the British, while reforms swept through Japan. All this was dry tinder for the spark of hope ignited by the discovery of riches in California.
People from around the world flocked to San Francisco in droves. Ships departed from docks in Europe and America groaning from the weight of passengers and mining equipment. Ship-crews immediately deserted upon reaching California’s shores, leaving boats abandoned and turning Yerba Buena Cove into a “forest of masts.” Townspeople in America’ s heartland headed west in wagon trains, leaving behind empty homes and shops with signs in their windows reading, “GONE TO THE DIGGINGS.”
In 1849, San Francisco’s population soared from 900 to 26,000. Another 100,000 people drifted through the area on their way into the California hills and hinterlands in search of their fortune. San Francisco crushed the equivalent of fifty years of growth and development into the course of a single year.
The effects of San Francisco’ s sudden gold boom did not escape the Kindred. While their elders continued their affairs in Europe and the Eastern Seaboard, the promise of wealth and blood offered by an overcrowded boomtown drew young vampires from across the nation. Ambitious Camarilla neonates saw the potential to create domains of their own, away from the stifling grip of their elders. Meanwhile, Sabbat packs and anarchs anticipated a new, unspoiled frontier where they could do as they pleased. The Kindred certainly found opportunities in San Francisco, where the arrival of a ship laden with heavy crates was commonplace. In a place where so many new people intermingled, hardly anyone noticed one or two strangers among thousands... or cared if a few of those new arrivals mysteriously vanished.
Although there was no gold in San Francisco itself, it was the largest port community near the gold fields, making it the destination of choice for disembarking prospectors. Although a few of them actually found gold, most didn’t. Instead, most of the money in the area was made in a more traditional fashion. It didn’t take long for the locals to discover that it was far more profitable catering to the miners and prospectors than searching for gold themselves. Shops, saloons and all manner of businesses sprang up in San Francisco, looking to serve the needs of the burgeoning population.
The abandoned ships in Yerba Buena Cove were put to good use in helping the city grow. The city fathers handled the problem by hauling the ships up onto the shore, where they were either broken up and used to construct new buildings and furniture or simply turned into buildings themselves. Cut a door or two in the hull of an overturned ship and you had a saloon. Many such structures sprang up along the harbor.
In the shadows between these new buildings and in the tent cities of the newcomers, the Kindred hunted with near abandon. Prospectors in the San Francisco Bay area fell victim to accidents, the elements, starvation and despair. They committed suicide at the rate of over 1,000 a year. It was not uncommon to stumble across a dried-up corpse bearing a pickaxe and shovel in the hills; common enough, in fact, that inquiry into the deaths were unheard of. Nobody cared how the poor wretch died.
The hunting was plentiful and good, so much so that vampires all but ignored the traditional conflicts between Camarilla and Sabbat while glutting themselves on the bounty of blood. Naturally, vampires fought over certain watering holes, but the conflicts simply demonstrated how easily they fell to their baser needs. Kindred and Cainite were all too similar in their bestial tendencies — except when the Sabbat and Camarilla sects stepped in to enforce opinion and policy. Regardless of allegiance, however, all vampires quickly learned to confine their hunting to the new city. The Lupines stalked the wilds outside San Francisco as guards encircling a prison. They shredded the first vampires to stray into their domain as a warning to the rest.
A Land of New Promise
Of course, new arrivals to San Francisco came not only from Europe, Mexico and the United States, but also from the Middle Kingdom. China’s Opium Wars against England and the ongoing encroachment of gweilo — white barbarians — everywhere strained the situation in the Far East. To many Chinese, California was Gum San, the “Golden Mountain,” a land of promise and opportunity away from war and starvation. Around the time of the Gold Rush, the first ship laden with some three hundred Chinese arrived in San Francisco.
Unfortunately, these immigrants discovered their “golden land of promise” was a rough frontier following the Golden Rule: Those with the gold make the rules. The Chinese remained a close-knit community even after their arrival, laying the foundations for San Francisco’ s modern Chinatown. Rather than becoming prospectors and miners (though some of them did), many Chinese found employment either serving the needs of San Francisco’s more fortunate inhabitants or working for the powerful railroad companies, who sought cheap labor to complete the transcontinental railroad.
Of course, with the Chinese and other Middle Kingdom immigrants came the Wan Kuei, the Ten Thousand Demons. It was not that the August Courts had any interest in a frontier city in a barbaric land, but the presence of some Kuei-jin was inevitable. A few, disgraced in shadow wars or fallen from favor in the August Courts, chose self-imposed exile over facing the Eye of Heaven and Final Death. Some found the freedom of the frontier exhilarating while others suffered in silence, hoping to redeem themselves and return to civilization. There were also those mortals who crossed the ocean only to die in their new land, fight their way free of torture in Yomi and take the Second Breath. More experienced Kuei-jin usually dealt with the resulting chih-mei.
Regardless of their reasons for coming to the Golden Mountain, though, the Wan Kuei who made the ocean crossing quickly discovered they were not alone in San Francisco’s nights.
The Kanbujian
In Chinatown’s early years, the Kuei-jin learned that leaving the Middle Kingdom behind did not necessarily free a soul from the weight dragging it down to Yomi after death. On occasion, a mortal of Chinese descent would take the Second Breath outside the bounds of civilization and away from the watchful eyes of the Kuei-jin jina and elders. With no aid from others of their kind and no knowledge of their nature, most of these poor unfortunates succumbed to their Demons, becoming ravening flesh-eaters that the Kuei-jin were forced to hunt down and destroy. On rare occasions, the Kin-jin discovered one of these chih-mei and destroyed it as a threat to the Masquerade, unaware of what it really was or where it originated.
The Wan Kuei called these poor wretches kànbujiàn — “unable to see” — because they were blind to Dharma and the path to the Hundred Clouds. If found soon enough, they were often able to master their P’o nature and join Kuei-jin society; if they failed or were not found in time, the Wan Kuei “mercifully” gave them Final Death. What the Kuei-jin did not know at first — and later refused to acknowledge — was that some rare kànbujiàn mastered their Demon nature on their own. Most did so by surrendering to the Yama Kings and becoming akuma, but a few struggled to find their own way, even discovering some Dharma principles through trial and error. Their Way was flawed and fraught with peril, but their determination was great.
East Meets West
The first encounters between Kuei-jin and San Francisco’s Kindred were brief and fleeting. The Kindred quickly discovered the clannish Chinese immigrants were better left alone. While most Europeans and Americans had abandoned such “childish” notions as vampires, the Chinese still maintained their old ways. The Kindred were surprised that Asians knew enough to take precautions against creatures of the night. Some of them — paper charms, rice scattered across thresholds and the like — were laughable. Others, such as prayer beads, charms backed by a true and abiding faith or the simple wisdom to huddle close to the light in groups, made the Chinese more difficult prey.
Of course, most Kindred created excuses not to bother rather than admit difficulty. “Chinese blood is thin and not as satisfying,” some said. “They’re not as vigorous, and less lively than other mortals.” “It’s a small loss, since there is so much already available.” Still, it vexed some Kindred to be denied anything. Some accepted the challenge by hunting more “interesting” prey in Chinatown... only to vanish and never be seen again.
Rumors circulated among the city’s vampires. They said the Chinese knew far more than they let on, luring Kindred into some kind of trap. Another whisper claimed that their numbers included mysterious magi or vampire- hunters. Yet others said that they had forged a pact with the Lupines, or they were host to a hitherto-unknown clan of Cainites . This last fiction was the closest to the truth.
The Wan Kuei needed the Chinese community to build Scarlet Screens in this new and alien land. To protect their interests, they destroyed any threat to Chinatown. In the process, the Demon People learned more about the White Demons dwelling among the Western mortals, the ones who came with the gweilo to the Middle Kingdom.
The first thing the Kuei-jin realized was that the Westerners were too numerous; they were too few to risk open confrontations. So the Wan Kuei remained in Chinatown’ s shadows and kept to their own affairs and council. They gave the gweilo vampires good reason to avoid their domain, but did not venture too far outside of it either. Those who disobeyed or threatened this version of the Kindred’ s Masquerade paid with their unlives.
Shadow Plays
Lawlessness ruled San Francisco’s streets in the years immediately following the Gold Rush. The population surge overtaxed the city’ s limited law enforcement, and bribery helped ensure the law looked the other way for almost anything. Along the waterfront rested saloons and whorehouses where miners spent their money, with roving gangs of criminals more than willing to help lighten their pockets.
One of the most notorious gangs was the Sydney Ducks, comprised of criminals who had escaped exile in Australia and made their way to California. They would waylay passers-by, throwing a bag over their heads and relieving them of their money and valuables (often leaving the victim dead or merely stunned with a strike from a sap or fist). The practice became known as “hooding” and the criminals who did it as “hoodlums.” The Australian gangsters also operated protection rackets in and along the Barbary Coast. The Sydney Ducks set fire to parts of the city five times for denying them tribute. It happened so often that Chinatown and Barbary Coast residents built exclusively with brick and stone rather than wood, so their homes and businesses would not burn so easily.
Some Kindred thought it too convenient that the depredations of the Sydney Ducks hurt businesses influenced by the Camarilla as well as burning out portions of Chinatown. Rumors claimed the gang was under the influence of a Sabbat pack or anarchs. Some even believed that its roster might have included vampires, though no proof of these conjectures ever manifested. The fires, however, did convince many local Kindred and Kuei-jin to find fireproof havens — a precaution that would prove vital a few decades later.
By the mid-1850s, miners had panned or mined out most of California’s surface gold, leaving only the deeper underground veins to be tapped. Those wise enough to invest their money carefully (including the Ventrue and other Camarilla vampires) funded large mining operations to dig out the gold that remained beyond the means and reach of individual miners. The continually expanding waterfront also became the mouth by which to feed the hungry factories of the East Coast and Europe. During that period, trading companies shipped every product workers could dig, drag, chop or tear from the mountains, fields and forests. The city became the premier center for commerce along the Pacific Ocean, finally drawing the attention of the elders and Princes that their childer had left behind years before. The unspoken truce between Camarilla, Sabbat and anarch vampires in San Francisco was over.
Of course, “peace” was a relative term. Kindred from all three factions struggled against each other previously, but mostly over territory and mortals. When the Transcontinental Railway became a reality, the Camarilla mentality reasserted itself. It was decided that San Francisco should be brought under the Camarilla’s aegis, to that ensure the Sabbat and anarchs would not control the city.
Public Vigilance
As usual, the Camarilla operated behind the scenes, using mortal proxies to carry out their plans. The Sabbat Cainites in 1850s San Francisco were wealthy and powerful. In very un-sect-like machinations, they influenced mortals — usually criminals — who in turn assumed positions of power locally during the Gold Rush and held them through graft, corruption and influence peddling. Ballot stuffing was practiced openly and an honest man’s vote counted for little. The common people , however, grew tired of this lawless state of affairs. Their desire to see justice was the Camarilla’s weapon against the Sabbat.
On June 9, 1851 in Sydney Cove, a man named John Jenkins simply walked into a merchant’s store, picked up the safe and walked away. He loaded the safe into a boat and calmly rowed out into the bay. Several of the merchant’s friends and associates pursued Jenkins and caught him easily, though he dumped the safe overboard. The public outcry was considerable.
Local citizens formed the Committee for Public Vigilance, which tried and executed Jenkins on its own authority. The Committee was very loosely organized at first, but its presence did give San Francisco’s criminals pause, at least for a short while. Jenkins’ boldness and the relative ease of his capture sent rumors among the Sabbat of a Camarilla plot, but local corruption ran deep. The Sabbat knew it would take more than a few outraged vigilantes to mobilize San Francisco’s citizens against its mortal power base.
It wasn’t long, however, before matters worsened. In 1855, there were nearly 500 murders in California but only 6 legal executions. Corrupt politicians maintained a tight hold on the government. Municipal spending was through the roof — much of it went into graft, bribes and embezzlement, lining the pockets of the city’s “civil servants.”
James King was a prominent San Francisco banker who had lost his fortune when local financial panic closed his bank. Outspoken against local corruption, he used his remaining money and the encouragement of his friends to found a newspaper voicing his opinions. In October of 1855, King began publication of the Evening Bulletin, a four-page paper. In it, he denounced criminals and political figures alike in fearless editorials that had people all over the city talking.
When notorious gambler Charles Cora shot and killed U.S. Marshal Richardson, he was “formally arrested” by friends of his who held public office. It was considered likely that he would walk away a free man. Following the incident, King ran an editorial saying that that if Cora wasn’t hanged, Sheriff David Scannell should take his place on the gallows.
King also took on city supervisor James Casey, revealing that Casey was a felon who had served time in Sing-Sing Prison in New York. In retribution, Casey shot King outside the Bulletin office on Montgomery Street. Witnesses rushed the wounded reporter to a doctor while Casey’s cronies in law-enforcement “took him into custody.”
In response to the shooting, over a thousand people turned out at the Montgomery Block in a show of support for James King. The crowd later made its way to the Plaza, where word circulated that the Committee for Public Vigilance was reforming. The following morning, members of the 1851 Committee met and created a new, more organized group. They penned an oath of fealty and assigned each member a number by which he would be known within the organization, to maintain anonymity. A few days later, the Committee consisted of some 3,500 members. In the meantime, however, James King died from his gunshot wound at home.
The Committee for Public Vigilance marched on the jail guarded by hundreds of local militia and law officers loyal to James Casey. Using a cannon to batter down the door, the Committee took Casey with little protest from his protectors. They also took gambler Charles Cora into custody. Both men received advocates and stood trial before a jury of Committee members, who summarily convicted the two men and sentenced them to a public hanging. An immense crowd filled Sacramento Street to watch the double execution, cementing the Committee for Public Vigilance’s power in the minds of San Franciscans.
Meanwhile, the Camarilla encouraged the Committee’s vigilantes to attack the Sabbat’s mortal proxies in the name of justice. They eliminated many of the Sabbat’s pawns from positions of power. The so-called revolution also hid the nightly movement of Camarilla scourges eliminating Sabbat targets and consigning vampires to ash. As far as the Camarilla was concerned, the strikes were clean and precise. They believed that they were the cause of the Sabbat’s fall in San Francisco. What they did not realize was the extent of the Sabbat’s internal dissent and scattered resources. The Sabbat were defeated as much by their own lack of foresight as the Camarilla’s attacks.
After the Committee’s cleanup of the city’s political echelons, legitimate businesses thrived — with the Camarilla riding their coattails. San Francisco formally incorporated as a city of some 30,000 people. The City by the Bay became reality, and the Inner Circle recognized the rule of Prince Jebediah Hawthorne in the Domain of San Francisco.
Emperor Norton
"At the preemptory request of a large majority of the citizens of these United States, I Joshua Norton, formerly of Algoa Bay, Cape of Good Hope, and now for the last nine years and ten months past of San Francisco, California, declare and proclaim myself the Emperor of These United States." — Joshua Norton, September 19, 1859
The first and only Emperor of the United States was born in London, England in 1819. He arrived in San Francisco by way of South Africa at the age of 30, with the sum of $40,000 to his name. Within five years, he’d lost that considerable fortune by speculating in real estate and attempting to corner the local market on rice. Living in poverty, Norton wrote a proclamation declaring himself Emperor of the United States. It was published in a local newspaper, at least in part due to the sheer novelty of the idea. He wore a uniform that he obtained from a second-hand store and walked the streets, administering to the daily needs of his “ domain.”
Emperor Norton issued various proclamations during his “reign,” including the abolition of the Democratic and Republican parties and a decree against using “the abominable word ‘Frisco,’ which has no linguistic or other warrant.” That alone carried a $25.00 fine. He also proposed the idea of a “League of Nations,” where the international community could settle its disputes (many years before the actual League of Nations signed its charter in San Francisco). He issued his own money, which he traded for legal tender; many stores came to accept Norton’ s currency as payment. He even mediated public disputes, defusing one anti-Chinese demonstration by quietly standing and reciting the Lord’s Prayer. His example shamed the demonstrators so greatly that they returned to their own affairs.
Idle speculation about Emperor Norton circulated among San Francisco’s Kindred. One account said he was the victim (or, perhaps, beneficiary) of Malkavian manipulation. Others suggested he was a puppet of one faction or another, or that he provided a useful spectacle for the mortal herd. Some even believed he was fey-touched. Whatever the case, vampires considered Norton inviolate because of his fame and public standing. He was left as a purely mortal phenomenon.
Norton died on January 8, 1880 on California Street. He was buried in the Masonic Cemetery, and his funeral procession ran two miles long. Between 10,000 and 30,000 people attended his funeral to bid farewell to America’ s first and only Emperor.
Paths of Iron
San Francisco continued to grow steadily through the next decade, remaining a key center of commerce for North America’ s entire West Coast. As gold mining dwindled, the discovery of the Comstock Silver Lode in Nevada sent a new infusion of wealth into San Francisco’s coffers. Many of the city’s most powerful mining magnates owned either the Nevada mines or the machines to properly drill them, setting up a continuous circle of wealth. The newfound prosperity further cemented the Camarilla’ s hold over the city, their only real victory of any substance in California. It was a bastion of influence amid a sea of Sabbat and anarch power.
San Francisco’s only limitation was its isolation from the rest of the United States. Out on the edge of the continent’s westernmost frontier, travel to and from the City by the Bay required East Coast ships to circumnavigate Cape Horn. The building of the Transcontinental Railroad in the 1860s rectified that problem by connecting the Pacific and Central rail lines.
Chinese immigrant workers did much of the hard labor required to extend the Pacific Line through the harsh Utah desert. This elicited jealousy from Caucasian workers, who grumbled that the Chinamen stole their jobs. The government responded by passing “coolie laws” that penalized the Chinese workers and made it hard for them to earn a living. It was only part of a prejudice against Chinese people that simmered and festered beneath the surface — occasionally erupting into accusations or even violence.
San Francisco’s Chinatown remained a city-within- a-city; people mostly kept to themselves, running their own schools and businesses and generally catering to the area’s inhabitants. In turn, the city government passed laws limiting “foreign” ownership of property. It also enacted laws taxing foreign (mainly Asian) workers more heavily, thus protecting jobs for “good Americans.” The situation suited Chinatown’s few Kuei-jin and shen, since it kept their havens secure from foreign devils and prevented expatriated Chinese from intermingling with local Westerners.
Black Bart, the Plundering PO8
One of the most notorious criminal figures of late 19th century San Francisco made his debut in August of 1877. The man who later became known as Black Bart stopped a Wells-Fargo stagecoach, leveled a double-barreled shotgun at the driver and uttered his famous command: “Throw down the box.” The driver surrendered the wooden strongbox, after which the robber allowed him to leave unharmed. The box turned up later, empty except for a poem scrawled on the back of a waybill:
“I’ve labored long and hard for bread —"
“For honor and for riches —"
“But on my corns too long you’ve tread,"
“You fine-haired sons of bitches."
It was signed: “Black Bart, the PO8.”
News of the mysterious Black Bart and his “po8try” spread quickly, though the robber himself remained out of sight for roughly a year afterward. When he finally resurfaced, he robbed another stagecoach, followed by several more. He always worked alone, apparently traveling on foot through the rough hills outside San Francisco. Wells- Fargo and the city placed a considerable reward of $800 on his head, but Black Bart remained at large.
Authorities didn’t capture Black Bart until 1883, when he was wounded in a stagecoach robbery. Although he escaped, he left his possessions behind. Investigators tracked him through the San Francisco laundry that cleaned his clothes, leading them to Charles Bolton, AKA “Black Bart.” Bolton confessed to the robbery, but the courts sentenced him to only six years in prison. He served a little over four.
At his release, reporters mobbed Bolton, looking to interview the infamous Black Bart. When asked if he planned to rob any more stagecoaches, he replied that he would not commit any further crimes. The questions continued, until one young reporter asked, ”One final question. Do you plan to write any more poetry?”
Bolton smiled and said, “Young man, didn’t you just hear me say I would commit no more crimes?”
Charles “Black Bart” Bolton left San Francisco heading south. He disappeared shortly thereafter and was never heard from again.
The Dragon Thrashes its Tail
"Fire has reclaimed to civilization and cleanliness the"
"Chinese ghetto, and no Chinatown will be permitted in the"
"borders of the city... it seems as though a divine wisdom"
"directed the range of the seismic horror and the range of the fire"
"god. Wisely, the worst was cleared away with the best."
— The Overland Monthly, 1906
On April 18, 1906 at 5:12 AM , Kuei-jin geomancers sensed a shift in the dragon-lines, a stirring of powerful forces — the Earth Dragon was restless, and a tremendous earthquake struck San Francisco in response . The quake itself lasted for less than a minute, but it toppled buildings and buckled streets. Broken gas mains and fallen lamps ignited fires that swept through the city.
The local fire department mobilized almost immediately, but the earthquake had ruptured all the water mains, leaving them to fight the fires with buckets instead of hoses. They retreated, hoping to contain the inferno and allow it to burn itself out. That, unfortunately, did not happen. The fires raged and spread, burning all of one day and into the next. They consumed some 28,000 buildings, including all of Chinatown.
Despite both the Kuei-jin’s and Kindred’s best precautions, the fires caught them all by surprise. A few vampires perished in the blaze, unable to flee without facing sunlight and frenzied by Rötschreck or wave soul. Retainers helped some Kindred escape from mansions on Nobility Hill, while other vampires sought refuge in the earth that had seemingly turned against the city. A handful remained underground for several nights, fearful of the heat they felt above their heads. The horror of being burned to kindling frightened one or two Kindred so greatly that they waited too long and sank into Torpor, where they lay to this night. Some sires tell their neonate progeny that on still nights, you can hear them, scratching at the underside of sidewalks and roads.
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers finally created a firebreak by dynamiting entire city blocks in the western districts. The blaze lasted for three days, as did the quake’s aftershocks. When it was all over, reporter Jack London wrote in a newspaper dispatch, “the City of San Francisco is no more.” The city was devastated, with some 3,000 people dead, 225,000 injured, vast numbers homeless and $400 million in damage (valued in 1906).
San Francisco’s vampire enclaves were in great disarray. Worse yet, with the mortal survivors huddled together for protection and comfort, hunting and feeding became exceedingly difficult. Forced to pick on lone stragglers and looters, many vampires turned on one another for vitae, sect be damned. The following weeks endured nightly destructions, with the strongest eliminating the weak . During the inevitable reconstruction, however, the Camarilla sent scourges into San Francisco to halt the indiscriminate feeding and make examples of Kindred who committed diablerie. The scourges caught and destroyed three Kindred, including one member of the primogen, but any other culprits either fled the region or hid their crime expertly.
The surviving Kuei-jin suffered the loss of their havens as well, and they would have to struggle against gweilo opposition (both mortal and Kin-jin) to regain it. Bereft of their sanctuaries , they hid among the mortal refugees of Chinatown as best they could, taking advantage of the deaths caused by the disaster to conceal their own feeding.
Some heralded Chinatown’s destruction as a blessing of sorts, and publicly hoped it would not be rebuilt.
Chinese and Western businessmen, however, planned to turn Chinatown into a tourist attraction — a unique part of San Francisco’s heritage that would draw people from around the world. The plan received the quiet support of Chinatown’s shen, including Father Li T’ien.
The city could not ignore the potential for prestige and income. Even Kindred who bothered concerning themselves with the “Chinatown problem” believed a tourist-town would eliminate the barriers the Asian enclave presented before. What they did not know was that the Kuei-jin chose to sacrifice their previous security for the opportunity to hide in plain sight.
In some ways, the fire and reconstruction following the Great Quake benefited both Cainites and Kuei-jin. With decades of influence among the wealthiest and most powerful mortals, the vampires subtly directed the reconstruction to suit their own needs. The rebuilt mansions on Nob Hill and the new Chinatown’s maze-like urban topography took shape under the watchful eyes of the city’ s oldest residents, with few people the wiser. The destruction of so many important papers and public records in the fire facilitated the flood of forged identities and birth certificates. In fact, a new wave of Chinese citizens known as “paper sons” gained their citizenship through such fake documents, swelling the local Asian population. Vampires “reset the clock” and established new, “legitimate” identities that withstood official scrutiny. The earthquake was a setback, but it would not keep San Francisco down.
Of cardinal importance to the Kuei-jin was that the earthquake revealed the shifting dragon lines in and around San Francisco. The shaking of the Earth Dragon’s tail released reservoirs of Chi that the Demon People tapped for their own purposes. They ensured that the new Chinatown controlled one such Dragon Nest. This life- force filled an invigorated San Francisco, thinned the Wall between worlds and drew the attention of other shen as well, who migrated to the city over the years. The Kin-jin remained largely ignorant of the geomantic implications of the quake, as the Kuei-jin hoped. Let the barbarians play at their petty struggles... the Demon People controlled San Francisco’s true power.
WHERE THE DEAD OUTNUMBER THE LIVING
"Such room to roam in after death!" — Joaquin Miller, speaking of the new graveyards in Colma
In 1901, San Francisco passed an ordinance banning any burials within the city. Land on the peninsula was simply too precious to waste on cemeteries. In fact, the city fathers encouraged the relocation of existing graveyards to outside the city, so that land currently allocated for cemeteries would be open for development. This need only increased following the 1906 earthquake and the city’ s reconstruction. Many landowners found it lucrative to move bodies to other plots and sell the land at a considerable profit (or, sometimes, to leave the interred bodies and sell the land anyway).
Between re-interring the previously deceased and the number of quake-related fatalities, it was a simple matter for a cart laden with caskets to move through San Francisco’s streets unnoticed. This allowed the city’s Kindred to go about the business of rebuilding and relocating with minimum duplicity during the years immediately before and after the reconstruction. Disturbing the graveyards also stirred the occasional ghost, drawing more psychics and mediums to the area.
Several new graveyards opened in the small town of Colma. In fact, the “town” consists mostly of cemeteries, with only a few homes and businesses for the cemetery attendants and other support services. Even tonight, Colma’s deceased far outnumber the living, a situation that draws the occasional Bone Flower, Giovanni or Samedi.
For Their Own Protection
After rebuilding, San Francisco settled into a seemingly quiet existence for the local Kindred and Kuei-jin. Anarchists found the City by the Bay less appealing than Los Angeles, but this was mostly thanks to the reconstruction process. Camarilla and Kuei-jin alike helped fund or support the city’ s restoration, thus claiming territory and businesses from the ground up. The Sabbat and anarchs, however, contributed little. Thus, they found themselves with no grip on the city whatsoever, be it socially, politically or financially.
Conflict between Kindred and Cainite in San Francisco was tame by comparison to domains like New York or Mexico City. Resultantly, the Camarilla’s reign over the region grew weak and decadent, raising concerns over Sabbat and anarch activities that local Kindred largely dismissed. San Francisco’s inhabitants were confident in their mastery of the night — confidence perhaps justified in the years following the quake, but that turned to unsupported arrogance as the years passed.
The city’s Kuei-jin, on the other hand, saw considerable activity in the first decades of the 20th century. Unrest in China sent thousands of rebellion- weary refugees across the sea, filling Chinatown’s already crowded streets. Occasionally, this deluge of mortals hid survivors from shadow wars and conflicts within the August Courts, fleeing the Middle Kingdom and seeking shelter in the West. These Kuei-jin — taught the formal manners and precise discipline of the Quincunx — were shocked by the laxity of North America’s kànbujiàn. The friction between traditionalists and Chinatown’ s undead inhabitants inevitably degenerated; shadow wars spilled over into conflicts between the city’s Tongs and associated criminals during the 1920s and ‘30s.
In December of 1941, the Empire of Japan attacked the United States Naval Base at Pearl Harbor, drawing the U.S. into World War II. In response, the American government displaced over a hundred thousand Japanese (two-thirds of them American citizens) from their homes to detainment camps in California, Utah and Idaho “for their own protection.” Many San Francisco gaki hid initially, while the army spirited their mortal screens and protection elsewhere. Eventually, however, the gaki realized that they were imprisoned as well. They possessed no freedom of movement, since no individuals of Japanese descent were supposed to be left behind.
When war workers and low-income families moved into the housing vacated by Japanese families, the gaki were forced to relocate. One or two gaki returned to Japan through the Yellow Springs, but most sought refuge in Chinatown. This latter lot suffered at the hands of their Chinese Kuei-jin hosts, who treated the gaki like slaves in retribution for Japan’ s invasion of the Middle Kingdom. Eventually, a few gaki escaped into the countryside, waiting for the matter to resolve. When the displaced Japanese returned, they found their homes and neighborhood occupied. Most resettled elsewhere. Japantown shrank from 30 blocks to a mere six.
Kuei-jin of Chinese descent capitalized on the Japanese deportations to eliminate or subjugate many of the gaki in San Francisco, deliberately ignoring the shadow war rules and requirements detailed under the Precepts of the War. What was the point, after all, since the August Courts were across the sea and thus could not appoint a ganshezhe (mediator) to oversee the conflict.
San Francisco was a pale reflection of the struggles transpiring in Nanking and Shanghai, but it was traumatic nonetheless. The city’s gaki population never truly recovered from the experience. Any Kuei-jin of Japanese extraction faces a difficult existence under the watchful eyes of San Francisco’s New Promise Mandarinate. Conversely, the Kuei-jin’s actions taught the gaki they could effectively play dirty pool in shadow wars, a trick they use to their advantage against the tradition-bound Mandarinate.
THE GREAT LEAP OUTWARD
As the 20th century drew to a close, signs and portents of an impending storm grew. In San Francisco, the status quo changed in ways few people anticipated, making the city a pivotal location in coming events.
The Dragon Wakes
In October of 1989, a powerful earthquake struck the San Francisco Bay Area incurring billions of dollars in damages and resulting in 63 deaths and numerous injuries. It thankfully did not spark the same terrible fires of 1906. In addition, most of the city’s buildings were constructed to resist earthquakes (although some “quake-proof” structures failed miserably). The event damaged portions of the city, however, including the Marina District and sections of the freeway and Bay Bridge.
To the citizens of San Francisco, the earthquake was a disaster. To local Kindred it was a nuisance, but also an opportunity to hide their activities in the resulting chaos and again influence reconstruction. To the Kuei-jin, it was something far more. The regional dragon lines shifted once more. The city’ s presence and continued growth polluted the wells of Chi in the area, sending out poison arrows that disturbed the slumbering Earth Dragon. The city’s life force waned, and the Kin-jin were bloated parasites feeding on its weakening Chi.
In the early 90s, Jochen Van Nuys was a junior member of a cabal of East Coast Ventrue, sent to San Francisco as their envoy. What Van Nuys found was a city of great wealth and potential ruled by a weak and ineffectual Prince, who did little to either keep the anarchs in check or even to enforce the Camarilla’s traditions. He also uncovered vampires existing in fear of the Prince and his primogen, squabbling over feeding territory and committing diablerie against each other in a dog-eat-dog struggle to survive. In short, he found a city of great potential that was ripe for a revolution. He decided to provide it.
By 1996, Van Nuys was ready to act. With allies back east as well as newfound local support, he executed a swift and masterful coup that deposed Prince Vannevar Thomas and his few remaining supporters. The Inner Circle was aware and tacitly approved of Van Nuys’ coup, backing his claim as the new Prince of San Francisco.
From the very first night he assumed power, Van Nuys walked a thin line. He replaced Thomas’ weak and ineffective leadership with decisiveness and action, but not so much as to rankle San Francisco’s anarchs or foster resistance against his rule. He guided with a firm but light touch, and San Francisco remained an unusually free and open city. Ventrue money followed in his wake, and San Francisco’s economy strengthened while the Ventrue’s coffers grew fatter.
The Two-Fang Serpent Plan
The first stirrings of San Francisco’s current woes began far from California’ s shores, in the August Courts of the Quincunx. In 1997, two of the five regional capitols of the August Courts were in foreign hands, with Hong Kong controlled by the Kin-jin and Shanghai under the gaki akuma of Japan. The “bamboo curtain” of Maoist China grew increasingly tattered. Western influences reverberated throughout the Middle Kingdom, carrying with them the influence of the Kin-jin. Elders and jina alike pointed to the impending Sixth Age and demanded something be done, while the Running Monkeys lived up to their names and strayed even further from tradition. The Bamboo Princes, in turn, demanded modernization and an abandonment of the ancient ways, practically courting the Demon Emperor’s arrival.
Two factions formed within the August Courts, each advocating their own plan of action. The Righteous Foreigner-Vanquishing Crusaders followed Mandarin Hao Wei-Liang, a cunning Resplendent Crane politician. It consisted of Resplendent Cranes, Devil-Tiger extremists and Thrashing Dragon hotheads. They called for a crusade to sweep the foreign devils from the shores of the Middle Kingdom and carry the battle to the unrighteous in their own lands. They proposed the Ash Plan as a means of accomplishing just that, which found support among Wan Kuei opportunists and those frustrated with the August Courts’ apparent weakness.
The Harmonious Menders of Broken Fences, led by Bone Flower elder Jiejie Li, proved more moderate. They claimed the Middle Kingdom needed to put its own house in order before beginning any crusades against the unrighteous. Corruption and evidence of the Yama Kings were rife in their own domains, yet the Foreigner- Vanquishing Crusaders would charge off to other lands, leaving their homes to rot from within. This was foolishness, the Fence-Menders said. The Crusaders countered by accusing their opponents of being cowards unwilling to take action while the world slid screaming into Hell.
The Menders of Broken Fences offered a compromise they called the Two-Fang Serpent Plan, which dealt with both the threats facing the Quincunx at home and abroad. The Kuei-jin directed the first “fang” toward securing the borders of the August Courts and dealing with dangers close at hand, like the occupations of Shanghai and Hong Kong. The plan’s second “fang” proposed taking and holding a western city to probe the Kin-jin’s strengths and abilities while establishing a foothold for a later time.
Shadow wars erupted between the two factions, each struggling to win the support of the August Courts. Finally, the Elders decided Hao Wei-Liang presented the greatest danger to their power and the Quincunx’s traditional ways. They chose the moderates’ plan, with some slight revisions. The August Courts created the Extraordinary Commission on the Rectification of Borders and appointed Jiejie Li its Ancestor, with experienced Devil Tiger General Chiu Bao as her lieutenant and First Oni. The Courts placed Hao Wei-Liang in command of a force known as the Glorious Ocean-Crossing Warriors, and charged him with capturing and pacifying Los Angeles, under the watchful eye of his rivals. The Ancestors would see whose approach proved more successful.
In the first days of 1998, scouts for the Ocean- Crossing Warriors entered Los Angeles, launching the Kuei-jin’s invasion. Initially things went smoothly. Kuei-jin warriors struck the Kin-jin like a hurricane, sweeping away loners and small, independent gangs of anarchs, while leaving the other Kindred scrambling for information and protection. By contrast, the Fence-Menders’ efforts in Shanghai and Hong Kong were slow and costly, both in terms of resources and the number of Kuei-jin who met Final Death. Hao Wei-Liang’s star was rising, to the concern of the August Courts’ Ancestors.
In 1999, however, a new star arose and changed everything. The red star known as the Eye of the Demon Emperor appeared in the heavens; it was believed an omen of the impending Sixth Age. Organized resistance spread among Los Angeles’ anarchs, sending Running Monkeys and war-wu to their Final Deaths in greater numbers. The Righteous Crusaders allied themselves with the spirits of the Yin World and the Yellow Springs, preparing a final, massive assault on Los Angeles from the Spirit Realms. In the midst of the attack, however, a storm of unprecedented fury struck the Yin World, smashing Kuei-jin and spectral forces alike. The Kin-jin pressed their advantage until, by summer, both sides were too exhausted to continue fighting.
Meanwhile, the Fence-Menders made considerable progress in Shanghai while maintaining a stalemate in Hong Kong. Jiejie Li also secured the defection of high-ranking Tremere Oliver Thrace, providing the August Courts with valuable information. Meanwhile, Hao Wei-Liang’ s troops were decimated and demoralized, his assault a failure in the eyes of his superiors. Ancestor Ch’ang of the Blood Court sent Hao an inkstone and calligraphic brush as a sign of his judgment. In late 1999, the Resplendent Crane Mandarin Hao met the Eye of Heaven with honor, leaving the Foreigner-Vanquishing Crusaders greatly weakened.
The invasion of Los Angeles sent shock-waves through the Anarch Free State and the Camarilla, which quickly moved to secure San Diego and San Francisco. Refugees from the fighting in LA sought shelter in Prince Van Nuys’ domain. He generously granted it, swelling the number of local anarchs. The Camarilla’s western princes strengthened their borders, looking to the Inner Circle for aid and waiting to see what the Cathayans would do next.
THE NEW PROMISE MANDARINATE
With the Final Death of Hao Wei-Liang, the Ancestors of the August Courts turned their attentions on Jiejie Li. Although the Fence-Menders won a considerable victory, Li knew full well she must now succeed where Hao failed, or she would follow him into the mouth of Yomi. If she were killed, the Ancestors could eliminate two powerful rivals and still reclaim Shanghai in the bargain. She didn’ t intend to allow them that opportunity.
As Li studied the situation, it became clear that a direct assault was no longer viable. The ranks of the Glorious Ocean-Crossing Warriors were severely thinned and morale was just as depleted. Elements loyal to the Foreigner-Vanquishing Crusaders also needed to be weeded out and replaced with jina and mandarins loyal to Li and the Fence-Menders. Li appointed Monkey Trip Wu ancestor of Los Angeles, with Mandarin Fun Toy of the Flatbush and Stockton Posse as his seconds-in-command. With that accomplished, she and Chiu Bao went to Los Angeles to oversee matters directly.
The new Kuei-jin strategy used a weapon from the arsenal of Western colonialism: divide and conquer. The Cathayans approached some of the prominent surviving anarch leaders and offered them a deal: their cooperation in exchange for aid in wiping out their closest rivals. It only took the agreement of a few to break the back of the anarch resistance and drive most of the surviving rebels out of the city. The Kuei-jin dubbed their alliance the “New Promise Mandarinate” and created a power structure that included both Wan Kuei and Kin-jin.
Jiejie Li presented this as a victory to the August Courts. Not only were the Kin-jin under control, but the Kuei-jin could civilize and teach them proper behavior, making them a useful resource in the coming struggle against the Sixth Age rather than chaff thrown to the winds.
To the Kindred of Los Angeles, the Mandarinate presented itself not as another process towards “enlightenment” or an egalitarian society, but as the fruition of those pursuits. It promised to upend the Camarilla’s status quo and offer advancement based on merit and ability rather than generation or diablerie. This strategy worked, leaving The Kuei-jin and their allies in control of Los Angeles. The Camarilla knew it would be a matter of time before the New Promise Mandarinate turned its attention elsewhere along North America’s Pacific Coast.
AN HONORABLE AGREEMENT
To forestall the Mandarinate’s expansion, the Inner Circle appointed Justicar Madame Guil to deal with “the Cathayan problem.” Of course the Camarilla’ s idea of confronting the situation was to sue for peace with the Cathayan invaders and cede Los Angeles to them. Hopefully this would keep them contained while the Camarilla dealt with a more pressing threat in the Sabbat. Theoretically, the justicar’s presence would also remind the western princes where their loyalties lay and help keep other cities from defecting to the New Promise Mandarinate.
Madame Guil and her entourage traveled across North America from Boston to San Francisco, dealing with several minor matters along the way and “marching out the flag” to rally the Camarilla’ s western holdings. Unfortunately, the local princes realized the Camarilla was essentially leaving them to the mercy of not just the Sabbat but also the Cathayans.
Once Guil established herself in San Francisco with Jochen Van Nuys unable to do anything save cooperate, negotiations with the New Promise Mandarinate began in earnest. To the Camarilla’ s surprise, the Cathayans eagerly discussed terms and welcomed the offer of a settlement. Negotiations took place throughout 2000, with meetings alternating between Los Angeles and San Francisco. Negotiators sent flurries of messages back to their superiors in the Camarilla and the Quincunx every step of the way, finally resulting in an acceptable agreement for both sides. The Kindred saved face by recognizing Kuei-jin authority in Asian matters and “approving” their recovery of the renegade domain of Los Angeles, allowing them to retain it so long as they kept “good and reasonable order” in the city. The Camarilla also agreed to compensate the Cathayans for the costs they incurred in “recovering” Los Angeles from the anarchs.
In short, the Camarilla capitulated, agreed to let the Cathayans keep what they’ d stolen and offered them a bribe in hopes they wouldn’t plunder any more territory. The Kuei-jin willingly allowed the Kin-jin to ascribe whatever face they wanted on the compromise, since it provided the Quincunx with significant gains — and even Western barbarians should be allowed to save face. The deal was set, but there was something on which neither side had counted.
THE WHEEL TURNS
Regardless of the Camarilla’s intentions, the western princes were not about to accept the Inner Circle’ s betrayal to Cathayans. Neither were the surviving anarchs driven from Los Angeles by the invaders. In the anarchs, the princes found the perfect tool. They would use one problem to solve another and, regardless the outcome, they would come out ahead. The plan called for the anarchs to execute a coup in San Francisco as the Camarilla’s delicate negotiations came to a close, eliminating both the Eastern and Western envoys. Once in control of the city, the anarchs could raise a force to move south and re-take Los Angeles with the backing of the western princes.
If the anarchs succeeded, they would eliminate or at least weaken the Cathayan threat and owe their success to their former political enemies. If they failed, the anarchs would be eliminated and the Camarilla would be forced into conflict with the so-called New Promise Mandarinate instead of suing for peace. Even if the Inner Circle discovered the culprits behind the coup, they would still need support to deal with the Cathayans (as well as the Sabbat). Any retribution would be minor at best and long in coming, even in the worst case scenario.
The details of the meeting between Kindred and Kuei-jin representatives on San Francisco’s Telegraph Hill are hazy, but what remains clear is that a well-armed force of anarchs attacked the meeting site. Many vampires met their Final Death that night with many more destroyed in the following hours. Accusations of betrayal and collaboration with the anarchs flew on both sides, as Prince Van Nuys watched his hopes of becoming the Camarilla’s peacemaker crumble.
THE TAKING OF SAN FRANCISCO
The August Courts graciously accepted the Camarilla’s tribute, then sent “envoys” and “peacekeepers” to San Francisco to ensure the safety of their own kind. In short order, the city’s Tremere and Toreador primogen met their Final Deaths at the hands of Kuei-jin assassins. The Wan Kuei swept into San Francisco like a black wind. It seemed nothing could stand before them. They seized control of the city’s prime areas, then opened “negotiations” with Prince Van Nuys and his surviving primogen.
Although couched in diplomacy, the Kuei-jin made it clear that the Kindred would be relocated to specific areas of San Francisco and allowed to exist under the watchful eye of the New Promise Mandarinate. Those who showed “merit” (i.e., loyalty to the new order) had the potential for advancement, while any threats would meet with swift retribution. The local Kindred had little choice; most complied with the invaders’ terms and moved their havens and strongholds to Cathayan-appointed areas.
After Van Nuys’ failure to hold the city, the Inner Circle stated they needed his diplomatic skills to “continue negotiations” with the Cathayans. They relieved him of his duties as prince, conferring that title on Sara Anne Winder, an ambitious and cunning Ventrue tactician charged with eventually re-taking the city.
In turn, the New Promise Mandarinate named Van Nuys Minister of the Office of Western Affairs, making him their official representative and mouthpiece for dealing with San Francisco’ s Kin-jin population. In their view, this places Van Nuys above Winder in the city’s hierarchy, even if many within the Camarilla don’t see it that way. It also secures the ousted Van Nuys’ loyalty for the New Promise Mandarinate.
Having taken the city, of course, the Fence-Menders now face the challenge of holding both Los Angeles and San Francisco while dealing with affairs at home. To worsen matters, the Quincunx expects them to expand their holdings in North America — against the better judgement of Jiejie Li and her advisors. The Two-Fang Serpent Plan is something of a victim of its own success, leaving the Kuei-jin stretched thin across California’s coast. The Kindred have regrouped from their early defeats, and the Camarilla now makes the Cathayans a greater priority than before. Robbed of the chance to gather intelligence while maintaining the element of surprise, the New Promise Mandarinate faces the prospect of organized resistance and an inevitable Camarilla counterattack while they fortify their holdings.
In San Francisco, these two powerful factions dance a delicate and dangerous diplomatic tango, each carefully hiding its weaknesses while ferreting out the enemy’s vulnerabilities and making plans for the future. On the city’ s fog-shrouded streets, Kuei-jin and Kindred encounter each other almost nightly, sometimes slipping past one another in the mist with the barest acknowledgment, other times exploding into violence that may eventually consume the city. As the pressure grows, each side can’ t help but reflect upon the prophecies of the End Times, watching the signs manifest all around them and wondering if hope still exists.
An Uneasy Peace
For thirteen years, a tentative peace held based upon the the Kuei-jin and Kindred joint awareness that war is bad for business and immortality. However, public peace, simply gave way to clandestine struggles in the shadows of skyscrapers and in the all concealing fog. Despite the regular, low-level internecine conflicts that consumed lesser domains within the city, the two primary powers kept the official peace. In 2014 a third party decided to shift the balance of power. Suddenly business fronts and havens were burning, peripheral Kuei-jin met the final death while prominent Kindred were diablerized and feral neonates were everywhere creating chaos enough to shatter the Masquerade - the Sabbat had returned with a vengeance. The Camarilla under Princess Winder and the New Promise Mandarinate under Jiejie Li were able to mount a counter offensive that while effective left both the Kindred and the Kuei-jin dangerously weak. In the aftermath, the surviving lords of the night cobbled together San Francisco by establishing five domains belonging to five theoretically equal barons. This political amalgam was never meant to last, but to the exhausted vampires of East and West, it was a welcome respite from the hell of war.
FIVE YEARS GONE
The city was preparing for another assault on the city by the Sabbat. Members of the Kindred and the Kuai-jin both ready to defend the city. The attack was expected at any time, but the attack did not come from the Sabbat but a completely unexpected enemy. In one day a great deal of the elders of the city were destroyed by a Government controlled group of hunters, including Jiejie Li and Sara Winder. In one 10 hour period the city was thrown into a desperate fight for survival. Most of the Kindred and Kuei-jin who lived stayed in hiding over several weeks.
When all was said and done, very few elders survived and the population of the city was cut in half. A rebuilding period slowly took place, Ancilla of the city were now the most powerful members of the city. The Sabbat had all but disappeared, their cities empty and notable figures gone. Members of the city found that if they were not careful with technology the hidden government organization would find and try to destroy them.
The balance of power changed again five years after the attack. Information was discovered that would give the person that had it enough power to rule the city. A young coterie of kindred decided to help the Brujah Baron, Sebastian Toc, get the information and rise to the princedom. The most powerful Kuei-jin, Cho of the Thrashing Dragons, became senechal. No one is saying what information gave Toc the power he needed.
Population
- -- City (883,305) - 2018
- -- Metro (4,729,484) - 2018
- -- CSA (9,666,055) - 2018
Arenas
Attractions
Bars and Clubs
- -- The Way Down -- A club known for its mixed supernatural clientèle.
- -- Laura - Waitress at the The Way down
- -- Dracula's Daughter -- A Kindred club that has admitted a number of other supernaturals.
- -- Gold Club -- High End Gentlemen's club
Cemeteries
-
- Pastor Father Andrew
- John (Gravedigger and Handyman)
- Jacob (Gravedigger and Handyman)
City Government
Crime
In 2011, 50 murders were reported, which is 6.1 per 100,000 people. There were about 134 rapes, 3,142 robberies, and about 2,139 assaults. There were about 4,469 burglaries, 25,100 thefts, and 4,210 motor vehicle thefts. The Tenderloin area has the highest crime rate in San Francisco: 70% of the city's violent crimes, and around one-fourth of the city's murders, occur in this neighborhood. The Tenderloin also sees high rates of drug abuse, gang violence, and prostitution. Another area with high crime rates is the Bayview-Hunters Point area. In the first six months of 2015 there were 25 murders compared to 14 in the first six months of 2014. However, the murder rate is still much lower than in past decades. That rate, though, did rise again by the close of 2016. According to the San Francisco Police Department, there were 59 murders in the city in 2016, an annual total that marked a 13.5% increase in the number of homicides (52) from 2015.
Gangs
Several street gangs operate in the city, including MS-13, the Sureños and Norteños in the Mission District,. African-American street gangs familiar in other cities, including the Crips, have struggled to establish footholds in San Francisco, while police and prosecutors have been accused of liberally labeling young African-American males as gang members. Criminal gangs with shotcallers in China, including Triad groups such as the Wo Hop To, have been reported active in San Francisco. In 1977, an ongoing rivalry between two Chinese gangs led to a shooting attack at the Golden Dragon restaurant in Chinatown, which left 5 people dead and 11 wounded. None of the victims in this attack were gang members. Five members of the Joe Boys gang were arrested and convicted of the crime. In 1990, a gang-related shooting killed one man and wounded six others outside a nightclub near Chinatown. In 1998, six teenagers were shot and wounded at the Chinese Playground; a 16-year-old boy was subsequently arrested.
Peace Officers
The San Francisco Police Department was founded in 1849.
The portions of Golden Gate National Recreation Area located within the city, including the Presidio and Ocean Beach, are patrolled by the United States Park Police.
The San Francisco Fire Department provides both fire suppression and emergency medical services to the city.
The city operates 22 public "pit stop" toilets.
The Angel Detective Agency
Citizens of the City
- Ernesto Albani --
- Gaëlle Biondi -- French Girl and former roommate
- Theudemar Donne -- Cannibal Cardiac Surgeon
- Rino Hathway -- Twenty Something R.A. from the University of San Francisco
- Tina Ó Nualláin -- Irish/American English Lit major who died of an overdose in the Church
Culture of the City
The Culture of San Francisco is major and diverse in terms of arts, music, cuisine, festivals, museums, and architecture but also is influenced heavily by Asian culture due to its large Asian population. San Francisco's diversity of cultures along with its eccentricities are so great that they have greatly influenced the country and the world at large over the years. In 2012, Bloomberg Businessweek voted San Francisco as America's Best City.
Music
Classical and Opera venues in San Francisco include the San Francisco Symphony, the San Francisco Opera and the San Francisco Ballet. They all perform at the San Francisco War Memorial and Performing Arts Center. San Francisco's Ballet and Opera are some of the oldest continuing performing arts companies in the United States. San Francisco is the birthplace and home city of the vocal ensemble Chanticleer. The city is also home to the American Conservatory Theater, also known as A.C.T., which has been routinely staging original productions since its arrival in San Francisco in 1967. Additionally, the New Conservatory Theater Center (NCTC) is known for being an intimate theater that routinely stages original productions by the local, national, and international LGBTQIA+ community. Hundreds of smaller, alternative theaters also attract a significant portion of the audience given their historical role in the San Francisco performing arts culture. The oldest of these are Intersection for the Arts, founded in 1965, and the Magic Theater, founded in 1967. A major player in the promotion of theater in the Bay Area is Theater Bay Area (or TBA). A non profit organization, Theater Bay Area has members from more than 365 Bay Area theater and dance companies, is the publisher of Callboard Magazine, and runs San Francisco's Half-Priced Ticket Booth.
The Herbst Theater stages an eclectic mix of music performances, as well as public radio's City Arts & Lectures.
The Fillmore is a music venue located in the Western Addition. It is the second incarnation of the historic venue that gained fame in the 1960s under concert promoter Bill Graham, housing the stage where now-famous musicians such as the Grateful Dead, Janis Joplin, Led Zeppelin and Jefferson Airplane first performed, fostering the San Francisco Sound. Beach Blanket Babylon is a zany musical revue and a civic institution that has performed to sold-out crowds in North Beach since 1974. Bimbo's 365 Club, in North Beach, is one of the city's oldest entertainment venues and plays host to music shows of all genres.
Additionally, San Francisco is home to the 200-member San Francisco Gay Men's Chorus, the world's first openly gay chorus, as well as the San Francisco Lesbian/Gay Freedom Band, the world's first[citation needed] openly gay musical organization. Two additional gay choruses, the Lesbian/Gay Chorus of San Francisco and Golden Gate Men's Chorus, also perform throughout the year.
Theater
San Francisco has a large number of theaters and live performance venues. Local theater companies have been noted for risk taking and innovation, as documented in the film Stage Left: A Story of Theater in San Francisco. The Tony Award-winning non-profit American Conservatory Theater (A.C.T.) is a member of the national League of Resident Theaters, and has been in San Francisco since it moved from Pittsburgh in 1967. Other local winners of the Regional Theater Tony Award include the San Francisco Mime Troupe, and Berkeley Rep in nearby Berkeley. The Magic Theater was the home theater of the playwright Sam Shepard during his most productive period, and many of his plays were first staged there. San Francisco-based SHN hosts productions of Broadway shows in its vintage 1920s-era venues in the Theater District: the Curran, Orpheum, and Golden Gate Theaters.
San Francisco has had a thriving improv theater community, with a distinctly different style of improv than much of the rest of the country[citation needed]. Unlike Chicago where one venue will host three 30-45 minute shows in one evening, most San Francisco improv shows are 2 hours long, complete with their own intermission. And while Chicago and New York are full of improv companies who perform formats based on the Harold (with multiple storylines going on at the same time), San Francisco is full of improv shows with single-story formats. Often referred to as play-length improv shows, these improv shows are rooted in the idea that if someone can perform something scripted (like a play, movie, or musical) then it can also be improvised just as well. Some groups that define the improvisation scene in San Francisco are: BATS Improv, The Un-Scripted Theater Company, and The San Francisco Improv Alliance.
Current Events
Fortifications
Galleries
Holy Ground
Hospitals
- Saint Francis Memorial Hospital
- Cynthia Spicer - High Security Terrorist attack survivor
- St. Mary's Medical Center (San Francisco) -- SMMC is the oldest continuously operating hospital in San Francisco.
Hotels & Hostels
Landmarks
- Alcatraz Island -- is home to the abandoned prison, the site of the oldest operating lighthouse on the West Coast of the United States, early military fortifications, and natural features such as rock pools and a seabird colony (mostly western gulls, cormorants, and egrets).
- Three Brother's Storage -- Owns several storage units inside office buildings in financial district
Maps
Mass Media
Missives
Monuments
Museums
The Museum of Modern Art (SFMOMA) contains 20th Century and contemporary pieces. It moved to its building in South of Market in 1995 and attracts 600,000 visitors annually.[2] The California Palace of the Legion of Honor contains primarily European works. The De Young Museum and the Asian Art Museum have significant anthropological and non-European holdings.
The Palace of Fine Arts, a remnant of the 1915 Panama-Pacific Exposition, used to house the Exploratorium, a popular science museum dedicated to teaching through hands-on interaction, which moved to a new location on the Embarcadero in 2013. The California Academy of Sciences is a natural history museum and hosts the Morrison Planetarium and Steinhart Aquarium. The Asian Art Museum of San Francisco has one of the most comprehensive collections of Asian art in the world. From 1958 until 2003 the collection was housed in a wing of at the original de Young in Golden Gate Park. When the de Young closed while constructing a new building, the Asian Art Museum moved to the former San Francisco City Library building, which was renovated for the purpose under the direction of Italian architect Gae Aulenti who had previously overseen the conversion of the Musée d'Orsay in Paris.
The San Francisco Zoo cares for a total of about 250 animal species, 39 of which have been deemed endangered or threatened.
Other museums include the Museum of the African Diaspora, the Contemporary Jewish Museum, the Museum of Craft & Folk Art, the Cartoon Art Museum, and the Mexican Museum. Some "offbeat" museums and galleries dealing in unconventional topics include the Antique Vibrator Museum, the Musée Mécanique (dedicated to penny arcade machines), the Museum of Ophthalmology, Ripley's Believe it or Not Museum, the Stamp Francisco/Stamp Art Gallery (rubber stamps not postal stamps), the Tattoo Art Museum (old tattoo machines and instruments), the UFO, Bigfoot and Loch Ness Monster Museum, and the Wax Museum at Fisherman's Wharf.
The Haas-Lilienthal House (2007 Franklin Street) is the only intact private Victorian-era home in San Francisco that is open to the public year-round and available for private functions.
Newspapers
- -- San Francisco Chronicle -- It is the only major daily paper covering the city and county of San Francisco. {Est. 1865}
Parks
Private Residences
Restaurants
Ruins
Schools
Shopping
- -- Doc's Comics & Collectables -- Owned by Dr. Diego "Doc" Soto, a PhD in both Criminal Justice and Civil War History, author of books on Alcatraz, comic book store owner, writer, and artist.
- Graven Goods -- A shop that sells only items belonging to dead people.
Strange Objects
- Apple Macintosh Portable M5120 Vintage Mac Laptop 1990 -- Laptop of Ghostly Communications
Telecommunications
Theaters
Transportation
Warehouses
Mages
- -- Penny Dreadful -- Born as Penelope Anne Drizkowski, is a mage and signature character of the Hollow Ones.
Vampires of the City
Court of San Francisco
 -- Sebastian Toc -- Brujah Prince
-- Sebastian Toc -- Brujah Prince -- Cho -- Seneschal -- Dance of the Thrashing Dragon
-- Cho -- Seneschal -- Dance of the Thrashing Dragon
Primogen of San Francisco
 -- Thalia Toreador Primogen
-- Thalia Toreador Primogen -- Tristram Ventrue Primogen
-- Tristram Ventrue Primogen -- Zen -- Bone Flowers -- Place: 8 Immortals Restaurant
-- Zen -- Bone Flowers -- Place: 8 Immortals Restaurant
Brujah
 --Angelica White -- (PC)
--Angelica White -- (PC) -- Amira - Brujah Bodyguard to Thalia
-- Amira - Brujah Bodyguard to Thalia -- Cord Brashen -- Sebastian's Muscle
-- Cord Brashen -- Sebastian's Muscle- [[]] -- Che Amaya -- Street Kid
Gangrel
 -- Esko -- Gangrel Elder
-- Esko -- Gangrel Elder -- Logan Wakefield -- Gangrel wanderer (Former PC) <<Now in Torpor>>
-- Logan Wakefield -- Gangrel wanderer (Former PC) <<Now in Torpor>> -- Liborio Tosetti (PC) [Morgan]
-- Liborio Tosetti (PC) [Morgan] -- Nannette Liborio's Child
-- Nannette Liborio's Child
Giovanni
- Diego -- Drug-dealer of Death
- Bob -- Black gang-banger who loves cocaine
- Jesus -- Hispanic gang-banger who is entranced with Everett
- Bob -- Black gang-banger who loves cocaine
Malkavian
 --Stephen Carvell -- (Mac PC)
--Stephen Carvell -- (Mac PC) -- Alban -- Sebastian's Accountant
-- Alban -- Sebastian's Accountant -- Delight -- Hacker?
-- Delight -- Hacker? -- Isaac Thompson -- Mob Doctor
-- Isaac Thompson -- Mob Doctor
Nosferatu
Ravnos
 -- Waraj Sind -- Ravnos Fixer
-- Waraj Sind -- Ravnos Fixer
Toreador
 -- Lorraine - Owner of The Way Down club
-- Lorraine - Owner of The Way Down club -- Quon Corbyn - Teen Hacker
-- Quon Corbyn - Teen Hacker -- Katia -- Sebastian's Second
-- Katia -- Sebastian's Second
Jade Dragons
Golden Dragons
 -- Zhou -- Negotiator for Zen
-- Zhou -- Negotiator for Zen
Vox Deorum
 -- Everett Young -- Anarch Musician {On Tour}
-- Everett Young -- Anarch Musician {On Tour}
 -- Justine McDavid -- New Child of Everett Young {On Tour}
-- Justine McDavid -- New Child of Everett Young {On Tour}
 --Annabel Nolan -- (Former PC)
--Annabel Nolan -- (Former PC)
Deceased or Missing
- -- Sara Anne Winder -- Ventrue Duke of San Francisco. {missing}
- -- Vannevar Thomas -- Former Ventrue prince of the city, {deceased}
- -- Bashe -- Destroyed by mortal hunters
The Baronies: Undead Territories
Places of Interest
- San Francisco State University -- San Francisco State University (commonly referred to as San Francisco State, SF State and SFSU) is a public university in San Francisco. As part of the 23-campus California State University system, the university offers 118 different bachelor's degrees, 94 master's degrees, and 5 doctoral degrees along with 26 teaching credentials among six academic colleges.
Coteries of San Francisco
- The New Crew -- An unofficial gang of neonates and fledglings that has recently sprung up.
Websites
---
---
https://environment.ambient-mixer.com/
---
---
https://washingtonmonthly.com/magazine/julyaugust-2012/the-power-broker/ {How politics really work in San Francisco}
---
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alcatraz_(TV_series)
---
---
---
https://www.onlyinyourstate.com/northern-california/san-francisco/abandoned-san-francisco/ {Abandoned San Francisco}
---
https://www.onlyinyourstate.com/author/sgarr/ {Visitor's guide to San Francisco}
---
https://www.travelchannel.com/shows/metropolis/photos/metropolis-san-francisco-then-and-now
---
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Culture_of_San_Francisco
---