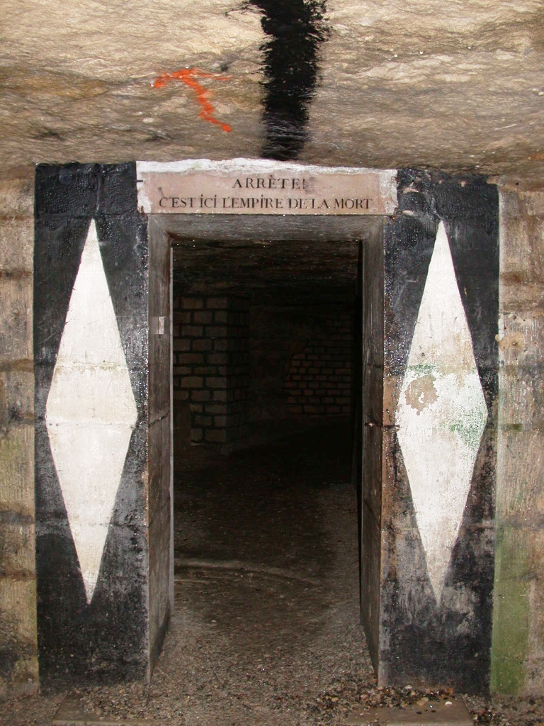
L'Ossuaire Municipal de Paris
Catacombes de Paris: An Introduction
The Catacombs of Paris are underground ossuaries in Paris, France which hold the remains of over six million people in a small part of the ancient Mines of Paris tunnel network. Located south of the former city gate "Barrière d’Enfer" (Gate of Hell) beneath Rue de la Tombe-Issoire, the ossuary was founded when city officials were faced with two simultaneous problems: a series of cave-ins starting in 1774 and overflowing cemeteries, particularly Saint Innocents. Nightly processions of bones from 1786 to 1788 transferred remains from cemeteries to the reinforced tunnels, and more remains were added in later years. The underground cemetery became a tourist attraction on a small scale from the early 19th century, and has been open to the public on a regular basis since 1874 with surface access from a building at Place Denfert-Rochereau.
The Catacombs are among the 14 City of Paris Museums managed by Paris Musées since January 1, 2013. The catacombs are formally known as l'Ossuaire Municipal or Catacombes officiels and have been called "The World's Largest Grave" due the number of individuals buried. Although the ossuary covers only a small section of the underground "les carrières de Paris" ("the quarries of Paris"), Parisians today often refer to the entire tunnel network as "the catacombs".
Une histoire des Os: The Birth of the Ossuaries
The Cemeteries of Paris
Paris' earliest burial grounds were to the southern outskirts of the Roman-era Left Bank city. In ruins after the Roman empire's 5th-century fall and the ensuing Frankish invasions, Parisians eventually abandoned this settlement for the marshy Right Bank: from the 4th century, the first known settlement there was on higher ground around a Saint-Etienne church and burial ground (behind today's Hôtel de Ville), and Right Bank urban expansion began in earnest after other ecclesiastical landowners filled in the marshlands from the late 10th century. Thus, instead of burying its dead away from inhabited areas as per usual human customs, the Paris Right Bank settlement began its life with cemeteries at its very center.
The most central of these cemeteries, a burial ground around the 5th-century Notre-Dame-des-Bois church, became the property of the Saint-Opportune parish after the original church was demolished by the 9th-century Norman invasions. When it became its own parish under the "Saints Innocents" church from 1130, this burial ground, filling the land between today's rue Saint-Denis, rue de la Ferronnerie, rue de la Lingerie and the rue Berger, had become the City's principal cemetery.
By the end of the same century "Saints Innocents" was neighbor to the principal Parisan Les Halles marketplace, and already filled to overflowing. To make room for more burials, the long-dead were exhumed and their bones packed into the roofs and walls of "charnier" galleries built to the inside of the cemetery walls. By the end of the 18th century, the central burial ground was a two metre high mound of earth filled with centuries of Parisian dead from disease, famine, and wars, plus the remains from the Hôtel-Dieu hospital and the Morgue; other Parisian parishes had their own burial grounds, but the conditions in Les Innocents cemetery were by far the worst.
A series of ineffective decrees limiting the use of the cemetery did little to remedy the situation, and it was not until the late 18th century that it was decided to create three new large-scale suburban burial grounds on the outskirts of the city, and to condemn all existing parish cemeteries within city limits.
The Former mines in Paris
The Left Bank rests upon rich Lutetian limestone deposits. This stone built much of the city, but it was extracted in suburban locations away from any habitation. Because of the post 12th-century haphazard mining technique of digging wells down to the deposit and extracting it horizontally along the vein until depletion, many of these (often illicit) mines were uncharted, and when depleted, often abandoned and forgotten. Paris had annexed its suburbs many times over the centuries, and by the 18th century many of its arrondissements (administrative districts) were or included previously mined territories.
The undermined state of the Left Bank was known to architects as early as the early 17th-century construction of the Val-de-Grâce hospital (most of its building expenses were sunk into its foundations), but a series of mine cave-ins beginning in 1774 with the collapse of a house along the "rue d'Enfer" (near today's crossing of the Avenue Denfert-Rochereau and the boulevard Saint-Michel) led King Louis XVI to name a commission to investigate the state of the Parisian underground. This led to the creation of the inspection Générale des Carrières (Inspection of Mines) service.
Le Mars des Morts: The Ossuary is Established
The need to eliminate Les Innocents gained urgency from May 30, 1780, when a basement wall in a property adjoining the cemetery gave way under the weight of the mass grave behind it. The cemetery was closed to the public and all "intra muros" (Latin: "within the city walls") burials were forbidden after 1780. The problem of what to do with the remains crowding "intra muros" cemeteries was still unresolved.
Mine consolidations were still under way and the underground around the site of the 1777 collapse that had initiated the project had already become a series of stone and masonry inspection passageways that reinforced the streets above. The mine renovation and cemetery closures were both issues within the jurisdiction of the Police Prefect Police Lieutenant-General Alexandre Lenoir, who had been directly involved in the creation of a mine inspection service. Lenoir was firmly behind an idea of moving Parisian dead to the newly renovated subterranean passageways that had been circulating since 1782. After deciding to further renovate the "Tombe-Issoire" passageways for their future role as an underground sepulchre, the idea became law in late 1785.
A well within a walled property above one of the principal subterranean passageways was dug to receive Les Innocents' unearthed remains, and the property itself was transformed into a sort of museum for all the headstones, sculptures and other artifacts recuperated from the former cemetery. Beginning from an opening ceremony on 7 April the same year, the route between Les Innocents and the "clos de la Tombe-Issoire" became a nightly procession of black cloth-covered wagons carrying the millions of Parisian dead. It would take two years to empty the majority of Paris cemeteries.
Cemeteries whose remains were moved to the Catacombs include Saints-Innocents (the largest by far with about 2 million buried over 600 years of operation), Saint-Étienne-des-Grès (one of the oldest), Madeleine Cemetery, Errancis Cemetery (used for the victims of the French Revolution), and Notre-Dame-des-Blancs-Manteaux.
