Hyde Park, Chicago: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Introduction == | |||
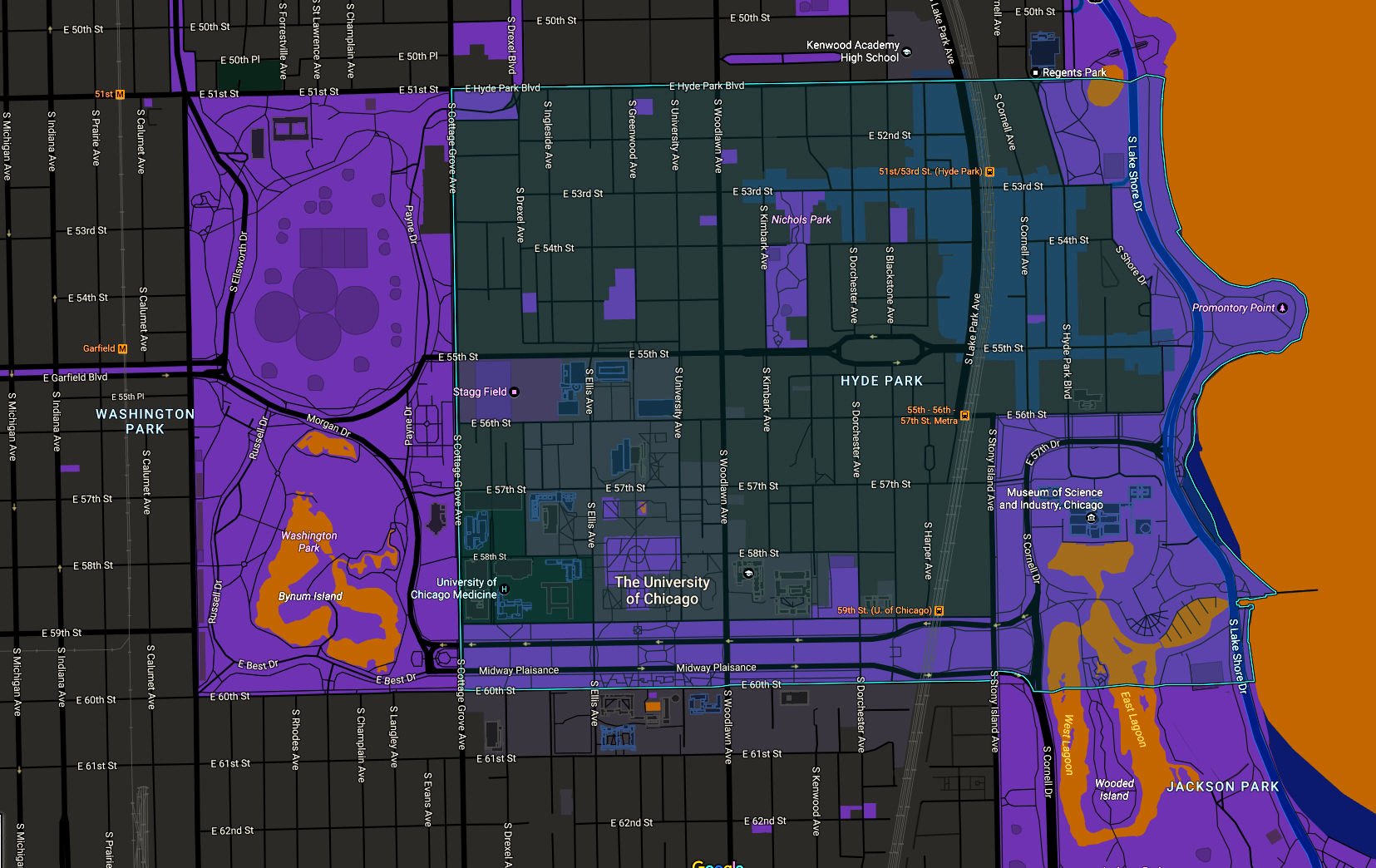
Hyde Park's official boundaries are 51st Street/Hyde Park Boulevard on the north, the Midway Plaisance (between 59th and 60th streets) on the south, Washington Park on the west, and Lake Michigan on the east. According to another definition, a section to the north between 47th Street and 51st Street/Hyde Park Boulevard is also included as part of Hyde Park, although this area is officially the southern part of the Kenwood community area. The area encompassing Hyde Park and the southern part of Kenwood is sometimes referred to as Hyde Park-Kenwood. | |||
Hyde Park hosts the University of Chicago and two of Chicago's four historic sites listed in the original 1966 National Register of Historic Places (Chicago Pile-1 and Robie House). In recent years, Hyde Park has received national attention as the longtime home of U.S. President Barack Obama. | |||
== History == | |||
=== Foundation through the Early Years === | |||
In 1853, Paul Cornell, a real estate speculator and cousin of Cornell University founder Ezra Cornell, purchased 300 acres (1.2 km2) of land between 51st and 55th streets along the shore of Lake Michigan, with the idea of attracting other Chicago businessmen and their families to the area. The land was located seven miles south of Downtown Chicago in a rural area that enjoyed weather tempered by the lake – cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter. It was conveniently located near the Illinois Central Railroad, which had been constructed two years earlier. Cornell successfully negotiated land in exchange for a railroad station at 53rd Street. Hyde Park quickly became a popular suburban retreat for affluent Chicagoans who wanted to escape the noise and congestion of the rapidly growing city. | |||
In 1857, the Hyde Park House, an upscale hotel, was built on the shore of Lake Michigan near the 53rd Street railroad station. For two decades, the Hyde Park House served as a focal point of Hyde Park social life. During this period, it was visited or lived in by many prominent guests, including Mary Todd Lincoln, who lived there with her children for two and a half months in the summer of 1865 (shortly after her husband was assassinated). The Hyde Park House burned down in an 1879 fire. The Sisson Hotel was built on the site in 1918 and was eventually converted into a condominium building (the Hampton House). | |||
In 1861, Hyde Park was incorporated as an independent township (called Hyde Park Township). Its boundaries were Pershing Road (39th Street) on the north, 138th Street on the south, State Street on the west, and Lake Michigan and the Indiana state line on the east. The territory of the township encompassed most of what is now the South Side of Chicago. Hyde Park Township remained independent of Chicago until it was annexed to the city in 1889. After annexation, the definition of Hyde Park as a Chicago neighborhood was restricted to the historic core of the former township, centered on Cornell's initial development between 51st and 55th streets near the lakefront. | |||
=== Late 19th through Early 20th Century Growth === | |||
In 1891 (two years after Hyde Park was annexed to the city of Chicago), the University of Chicago was established in Hyde Park through the philanthropy of John D. Rockefeller and the leadership of William Rainey Harper. The University of Chicago eventually grew into one of the world's most prestigious universities, and is now associated with eighty-nine Nobel Prize laureates. | |||
In 1893, Hyde Park hosted the World's Columbian Exposition (a world's fair marking the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus' arrival in the New World). The World's Columbian Exposition brought fame to the neighborhood, which gave rise to an inflow of new residents and spurred new development that gradually started transforming Hyde Park into a more urban area. However, since most of the structures built for the fair were temporary, it left few direct traces in the neighborhood. The only major structure from the fair that is still standing today is Charles Atwood's Palace of Fine Arts, which has since been converted into the Museum of Science and Industry. | |||
In the early decades of the twentieth century, many upscale hotels were built in Hyde Park (mostly along the lakefront). Hyde Park became a popular resort area in Chicago. Most of these hotels closed during the Great Depression, and were eventually converted into apartment and condominium buildings (most of which are still standing today). | |||
Historical images of Hyde Park can be found in Explore Chicago Collections, a digital repository made available by Chicago Collections archives, libraries and other cultural institutions in the city. | |||
=== Racial Integration / Economic Decline / & Urban Renewal === | |||
Until the middle of the twentieth century, Hyde Park remained an almost exclusively white neighborhood (despite its proximity to Chicago's Black Belt). Hyde Parkers relied on racially restrictive covenants to keep African Americans out of the neighborhood. At the time, the use of such covenants was supported by the University of Chicago. | |||
After the Supreme Court banned racially restrictive covenants in 1948, African Americans began moving into Hyde Park, and the neighborhood gradually became multiracial. In 1955, civil rights activist Leon Despres was elected alderman of Hyde Park and held the position for twenty years. Despres argued passionately for racial integration and fair housing on the floor of the Chicago City Council, and became known as the "liberal conscience of Chicago" for often casting the sole dissenting vote against the policies of Chicago's then-mayor Richard J. Daley. | |||
During the 1950s, Hyde Park experienced economic decline as a result of the white flight that followed the rapid inflow of African Americans into the neighborhood. In the 1950s and 1960s, the University of Chicago, in its effort to counteract these trends, sponsored one of the largest urban renewal plans in the nation. The plan involved the demolition and redevelopment of entire blocks of decayed buildings with the goal of creating an "interracial community of high standards." | |||
After the plan was carried out, Hyde Park's average income soared by seventy percent, but its African American population fell by forty percent, since the substandard housing primarily occupied by low-income African Americans had been purchased, torn down, and replaced, with the residents not being able to afford to remain in the newly rehabilitated areas. The ultimate result of the renewal plan was that Hyde Park did not experience the economic depression that occurred in the surrounding areas and became a racially integrated middle-class neighborhood. | |||
== Subdivisions == | |||
=== University of Chicago campus === | |||
The part of Hyde Park bounded by 55th Street on the north, the Midway Plaisance on the south, Washington Park on the west, and the Metra line on the east is the official territory of the University of Chicago campus. Most of the university's major facilities are located within the western half of this area (west of University Avenue). The part of the campus east of University Avenue is mostly residential, with many of its residents being University of Chicago faculty. | |||
=== East Hyde Park === | |||
The part of Hyde Park located east of the Metra line is called East Hyde Park. This area has a large number of high-rise condominiums, many of them facing the lakefront. In this respect, East Hyde Park differs markedly from the rest of Hyde Park, where the vast majority of the residential structures are three-story apartment buildings and single-family homes, with only a small number of high-rise condominiums. | |||
=== Kenwood === | |||
The area bounded by 47th Street on the north, 51st Street/Hyde Park Boulevard on the south, Cottage Grove Avenue on the west, and Lake Michigan on the east is officially the southern part of the Kenwood community area, but it is often unofficially considered to be part of Hyde Park due to the shared culture and history of the two areas. The name Hyde Park-Kenwood is sometimes applied to the area encompassing Hyde Park and the southern part of Kenwood. The southern part of Kenwood is notable for its many luxurious mansions, which were built at the end of the nineteenth and the beginning of the twentieth centuries for wealthy Chicagoans. A number of prominent Chicagoans currently reside in this area. In particular, a mansion on the corner of Greenwood Avenue and 51st Street/Hyde Park Boulevard (on the southern edge of Kenwood) has been the home of U.S. President Barack Obama since 2005. A mansion on the corner of Woodlawn Avenue and 49th Street was built for Nation of Islam leader Elijah Muhammad and is currently owned by his successor Louis Farrakhan. In addition, there is a mansion in the 4900 block of Woodlawn Avenue that was once the home of boxing legend Muhammad Ali. | |||
== Racial Diversity == | |||
Hyde Park is one of Chicago's most racially diverse neighborhoods. Its population is 46.7% White, 30.4% African American, 12.4% Asian American, 6.3% Hispanic, and 4.1% of other races or of more than one race. There are significant differences between the racial demographics of the part of Hyde Park south of 55th Street (most of which is part of the University of Chicago campus) and the part of Hyde Park north of 55th Street. Residents south of 55th Street are predominantly White and Asian American, with only a relatively small percentage being African American. North of 55th Street, on the other hand, African Americans make up approximately half of the population. The population of the northwestern corner of Hyde Park (north of 55th Street and west of Drexel Avenue) is almost 100% African American. | |||
Hyde Park's location in the center of the predominantly African American South Side of Chicago as well as its large population of well-to-do African American residents have made it an important cultural and political hub of Chicago's African American community. Many of Chicago's prominent African American politicians, including former Chicago Mayor Harold Washington, former U.S. Senator Carol Moseley Braun, and U.S. President Barack Obama, currently live or have in the past lived in Hyde Park. | |||
=== Liberal Politics === | |||
Hyde Parkers of all racial backgrounds are known for being staunchly liberal in their political views. About 95% of the residents vote for Democratic candidates in general elections. | |||
== Landmarks == | |||
The following Hyde Park community area properties have been added to the National Register of Historic Places: Chicago Beach Hotel, Arthur H. Compton House, East Park Towers, Chicago Pile-1, Flamingo-on-the-Lake Apartments, Isadore H. Heller House, Charles Hitchcock Hall, Hotel Del Prado, Hotel Windermere East, Frank R. Lillie House, Robert A. Millikan House, Poinsettia Apartments, Promontory Apartments, Frederick C. Robie House, George Herbert Jones Laboratory, St. Thomas Church and Convent, Shoreland Hotel, German submarine U-505, and University Apartments. | |||
In addition, the NRHP Hyde Park-Kenwood Historic District and Jackson Park Historic Landscape District and Midway Plaisance are located, at least in part, within the Hyde Park community area. | |||
== Parks == | |||
=== Promontory Point === | |||
Promontory Point is a man-made peninsula that extends out into Lake Michigan at 55th Street, providing spectacular views of the Downtown Chicago skyline to the north. Promontory Point is a popular location for picnicking, sunbathing, and swimming. It recently made news as the location of the wedding reception between George Lucas and Mellody Hobson in June 2013. | |||
=== Jackson Park === | |||
The southeastern corner of Hyde Park contains the northern end of Jackson Park. Jackson Park consists of lagoons surrounding an island in the middle (called the Wooded Island), on which a small Japanese garden is located. It is home to a large population of beavers and over two dozen species of birds. The Midway Plaisance, a wide boulevard that runs from Stony Island Avenue to Cottage Grove Avenue between 59th and 60th streets, connects Jackson Park to Washington Park (located to the west of Hyde Park). | |||
== Shopping Districts == | |||
53rd, 55th, and 57th streets host most of the businesses in Hyde Park. | |||
=== 53rd Street === | |||
53rd Street is Hyde Park's oldest shopping district, lined with many small businesses and restaurants offering various dining options. Harper Court, a small-business-oriented shopping center, extends north of 53rd Street along Harper Avenue. A farmers' market is held there in the summer. | |||
=== 55th Street === | |||
The segment of 55th Street between the Metra line and the lake offers a series of ethnic restaurants serving Thai, Japanese, and Korean cuisine. To the west of the Metra line between 54th and 55th streets lies the Hyde Park Shopping Center. The shopping center is anchored by the Treasure Island grocery store, and also includes a Walgreens, Ace Hardware, Office Depot, Potbelly Sandwich Works, the Bonjour Bakery and Cafe, and an upscale French restaurant called "La Petite Folie." | |||
=== 57th Street === | |||
57th Street is noted for its independent bookstores, including the South Side branch of Powell's and the general-readership branch of the Seminary Co-op bookstore, known as "57th Street Books." 57th Street also offers the Medici Restaurant and Bakery, Z&H Cafe, and the Salonica Restaurant, along with small grocery stores, hair stylists, and dry cleaners. On the first weekend in June, the venerable 57th Street Art Fair takes up 57th Street between Kimbark and Kenwood avenues. | |||
== Museums == | |||
* -- [[DuSable Museum of African American History]] (located just outside Hyde Park on the eastern edge of Washington Park) | |||
* -- [[Hyde Park Art Center]] | |||
* -- [[Museum of Science and Industry]] | |||
* -- [[Oriental Institute]] – an archaeology museum (mostly focusing on the ancient Near East) within the University of Chicago. | |||
* -- [[Smart Museum of Art]] – an art museum within the University of Chicago. | |||
== Institutions of Higher Education == | |||
* -- [[Catholic Theological Union]] – a seminary of Roman Catholic religious orders and lay women and men. | |||
* -- [[Chicago Theological Seminary]] – a seminary of the United Church of Christ. | |||
* -- [[Lutheran School of Theology at Chicago]] – a seminary of the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America. | |||
* -- [[McCormick Theological Seminary]] – a seminary of the Presbyterian Church. | |||
* -- [[University of Chicago]] – a private research university. | |||
* -- [[University of Chicago Laboratory Schools]] – a private coeducational nursery-12 school founded by educational reformer John Dewey in 1896. | |||
== Houses of Worship == | |||
* -- St. Thomas Church and Convent | |||
* -- Rockefeller Chapel | |||
* -- First Unitarian Church of Chicago | |||
* -- KAM Isaiah Israel | |||
* -- The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints | |||
* -- The First Baptist Church of Chicago the oldest Baptist church in the city | |||
* -- Hyde Park Union Church | |||
* -- Congregation Rodfei Zedek | |||
* -- Rohr Chabad at the University of Chicago and Hyde Park | |||
== Transportation == | |||
Hyde Park is connected to the rest of the city by CTA buses and the Metra Electric Line. CTA buses provide express service to the downtown, and they also allow transfers to Red Line and Green Line trains to the Loop. The Metra Electric Line, which uses the tracks of the former Illinois Central Railroad, has several stops in Hyde Park and provides service to Millennium Station in the downtown. | |||
=== CTA bus services === | |||
* -- #2 Hyde Park Express | |||
* -- #4 Cottage Grove | |||
* -- #6 Jackson Park Express | |||
* -- #10 Museum of Science and Industry | |||
* -- #15 Jeffery Local | |||
* -- #28 Stony Island | |||
* -- #55 Garfield | |||
=== Additional CTA bus services, paid for by the University of Chicago === | |||
* -- #171 University of Chicago/Hyde Park | |||
* -- #172 University of Chicago/Kenwood | |||
* -- #192 University of Chicago Hospitals Express | |||
Revision as of 13:37, 22 October 2016
Introduction
Hyde Park's official boundaries are 51st Street/Hyde Park Boulevard on the north, the Midway Plaisance (between 59th and 60th streets) on the south, Washington Park on the west, and Lake Michigan on the east. According to another definition, a section to the north between 47th Street and 51st Street/Hyde Park Boulevard is also included as part of Hyde Park, although this area is officially the southern part of the Kenwood community area. The area encompassing Hyde Park and the southern part of Kenwood is sometimes referred to as Hyde Park-Kenwood.
Hyde Park hosts the University of Chicago and two of Chicago's four historic sites listed in the original 1966 National Register of Historic Places (Chicago Pile-1 and Robie House). In recent years, Hyde Park has received national attention as the longtime home of U.S. President Barack Obama.
History
Foundation through the Early Years
In 1853, Paul Cornell, a real estate speculator and cousin of Cornell University founder Ezra Cornell, purchased 300 acres (1.2 km2) of land between 51st and 55th streets along the shore of Lake Michigan, with the idea of attracting other Chicago businessmen and their families to the area. The land was located seven miles south of Downtown Chicago in a rural area that enjoyed weather tempered by the lake – cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter. It was conveniently located near the Illinois Central Railroad, which had been constructed two years earlier. Cornell successfully negotiated land in exchange for a railroad station at 53rd Street. Hyde Park quickly became a popular suburban retreat for affluent Chicagoans who wanted to escape the noise and congestion of the rapidly growing city.
In 1857, the Hyde Park House, an upscale hotel, was built on the shore of Lake Michigan near the 53rd Street railroad station. For two decades, the Hyde Park House served as a focal point of Hyde Park social life. During this period, it was visited or lived in by many prominent guests, including Mary Todd Lincoln, who lived there with her children for two and a half months in the summer of 1865 (shortly after her husband was assassinated). The Hyde Park House burned down in an 1879 fire. The Sisson Hotel was built on the site in 1918 and was eventually converted into a condominium building (the Hampton House).
In 1861, Hyde Park was incorporated as an independent township (called Hyde Park Township). Its boundaries were Pershing Road (39th Street) on the north, 138th Street on the south, State Street on the west, and Lake Michigan and the Indiana state line on the east. The territory of the township encompassed most of what is now the South Side of Chicago. Hyde Park Township remained independent of Chicago until it was annexed to the city in 1889. After annexation, the definition of Hyde Park as a Chicago neighborhood was restricted to the historic core of the former township, centered on Cornell's initial development between 51st and 55th streets near the lakefront.
Late 19th through Early 20th Century Growth
In 1891 (two years after Hyde Park was annexed to the city of Chicago), the University of Chicago was established in Hyde Park through the philanthropy of John D. Rockefeller and the leadership of William Rainey Harper. The University of Chicago eventually grew into one of the world's most prestigious universities, and is now associated with eighty-nine Nobel Prize laureates.
In 1893, Hyde Park hosted the World's Columbian Exposition (a world's fair marking the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus' arrival in the New World). The World's Columbian Exposition brought fame to the neighborhood, which gave rise to an inflow of new residents and spurred new development that gradually started transforming Hyde Park into a more urban area. However, since most of the structures built for the fair were temporary, it left few direct traces in the neighborhood. The only major structure from the fair that is still standing today is Charles Atwood's Palace of Fine Arts, which has since been converted into the Museum of Science and Industry.
In the early decades of the twentieth century, many upscale hotels were built in Hyde Park (mostly along the lakefront). Hyde Park became a popular resort area in Chicago. Most of these hotels closed during the Great Depression, and were eventually converted into apartment and condominium buildings (most of which are still standing today).
Historical images of Hyde Park can be found in Explore Chicago Collections, a digital repository made available by Chicago Collections archives, libraries and other cultural institutions in the city.
Racial Integration / Economic Decline / & Urban Renewal
Until the middle of the twentieth century, Hyde Park remained an almost exclusively white neighborhood (despite its proximity to Chicago's Black Belt). Hyde Parkers relied on racially restrictive covenants to keep African Americans out of the neighborhood. At the time, the use of such covenants was supported by the University of Chicago.
After the Supreme Court banned racially restrictive covenants in 1948, African Americans began moving into Hyde Park, and the neighborhood gradually became multiracial. In 1955, civil rights activist Leon Despres was elected alderman of Hyde Park and held the position for twenty years. Despres argued passionately for racial integration and fair housing on the floor of the Chicago City Council, and became known as the "liberal conscience of Chicago" for often casting the sole dissenting vote against the policies of Chicago's then-mayor Richard J. Daley.
During the 1950s, Hyde Park experienced economic decline as a result of the white flight that followed the rapid inflow of African Americans into the neighborhood. In the 1950s and 1960s, the University of Chicago, in its effort to counteract these trends, sponsored one of the largest urban renewal plans in the nation. The plan involved the demolition and redevelopment of entire blocks of decayed buildings with the goal of creating an "interracial community of high standards."
After the plan was carried out, Hyde Park's average income soared by seventy percent, but its African American population fell by forty percent, since the substandard housing primarily occupied by low-income African Americans had been purchased, torn down, and replaced, with the residents not being able to afford to remain in the newly rehabilitated areas. The ultimate result of the renewal plan was that Hyde Park did not experience the economic depression that occurred in the surrounding areas and became a racially integrated middle-class neighborhood.
Subdivisions
University of Chicago campus
The part of Hyde Park bounded by 55th Street on the north, the Midway Plaisance on the south, Washington Park on the west, and the Metra line on the east is the official territory of the University of Chicago campus. Most of the university's major facilities are located within the western half of this area (west of University Avenue). The part of the campus east of University Avenue is mostly residential, with many of its residents being University of Chicago faculty.
East Hyde Park
The part of Hyde Park located east of the Metra line is called East Hyde Park. This area has a large number of high-rise condominiums, many of them facing the lakefront. In this respect, East Hyde Park differs markedly from the rest of Hyde Park, where the vast majority of the residential structures are three-story apartment buildings and single-family homes, with only a small number of high-rise condominiums.
Kenwood
The area bounded by 47th Street on the north, 51st Street/Hyde Park Boulevard on the south, Cottage Grove Avenue on the west, and Lake Michigan on the east is officially the southern part of the Kenwood community area, but it is often unofficially considered to be part of Hyde Park due to the shared culture and history of the two areas. The name Hyde Park-Kenwood is sometimes applied to the area encompassing Hyde Park and the southern part of Kenwood. The southern part of Kenwood is notable for its many luxurious mansions, which were built at the end of the nineteenth and the beginning of the twentieth centuries for wealthy Chicagoans. A number of prominent Chicagoans currently reside in this area. In particular, a mansion on the corner of Greenwood Avenue and 51st Street/Hyde Park Boulevard (on the southern edge of Kenwood) has been the home of U.S. President Barack Obama since 2005. A mansion on the corner of Woodlawn Avenue and 49th Street was built for Nation of Islam leader Elijah Muhammad and is currently owned by his successor Louis Farrakhan. In addition, there is a mansion in the 4900 block of Woodlawn Avenue that was once the home of boxing legend Muhammad Ali.
Racial Diversity
Hyde Park is one of Chicago's most racially diverse neighborhoods. Its population is 46.7% White, 30.4% African American, 12.4% Asian American, 6.3% Hispanic, and 4.1% of other races or of more than one race. There are significant differences between the racial demographics of the part of Hyde Park south of 55th Street (most of which is part of the University of Chicago campus) and the part of Hyde Park north of 55th Street. Residents south of 55th Street are predominantly White and Asian American, with only a relatively small percentage being African American. North of 55th Street, on the other hand, African Americans make up approximately half of the population. The population of the northwestern corner of Hyde Park (north of 55th Street and west of Drexel Avenue) is almost 100% African American.
Hyde Park's location in the center of the predominantly African American South Side of Chicago as well as its large population of well-to-do African American residents have made it an important cultural and political hub of Chicago's African American community. Many of Chicago's prominent African American politicians, including former Chicago Mayor Harold Washington, former U.S. Senator Carol Moseley Braun, and U.S. President Barack Obama, currently live or have in the past lived in Hyde Park.
Liberal Politics
Hyde Parkers of all racial backgrounds are known for being staunchly liberal in their political views. About 95% of the residents vote for Democratic candidates in general elections.
Landmarks
The following Hyde Park community area properties have been added to the National Register of Historic Places: Chicago Beach Hotel, Arthur H. Compton House, East Park Towers, Chicago Pile-1, Flamingo-on-the-Lake Apartments, Isadore H. Heller House, Charles Hitchcock Hall, Hotel Del Prado, Hotel Windermere East, Frank R. Lillie House, Robert A. Millikan House, Poinsettia Apartments, Promontory Apartments, Frederick C. Robie House, George Herbert Jones Laboratory, St. Thomas Church and Convent, Shoreland Hotel, German submarine U-505, and University Apartments.
In addition, the NRHP Hyde Park-Kenwood Historic District and Jackson Park Historic Landscape District and Midway Plaisance are located, at least in part, within the Hyde Park community area.
Parks
Promontory Point
Promontory Point is a man-made peninsula that extends out into Lake Michigan at 55th Street, providing spectacular views of the Downtown Chicago skyline to the north. Promontory Point is a popular location for picnicking, sunbathing, and swimming. It recently made news as the location of the wedding reception between George Lucas and Mellody Hobson in June 2013.
Jackson Park
The southeastern corner of Hyde Park contains the northern end of Jackson Park. Jackson Park consists of lagoons surrounding an island in the middle (called the Wooded Island), on which a small Japanese garden is located. It is home to a large population of beavers and over two dozen species of birds. The Midway Plaisance, a wide boulevard that runs from Stony Island Avenue to Cottage Grove Avenue between 59th and 60th streets, connects Jackson Park to Washington Park (located to the west of Hyde Park).
Shopping Districts
53rd, 55th, and 57th streets host most of the businesses in Hyde Park.
53rd Street
53rd Street is Hyde Park's oldest shopping district, lined with many small businesses and restaurants offering various dining options. Harper Court, a small-business-oriented shopping center, extends north of 53rd Street along Harper Avenue. A farmers' market is held there in the summer.
55th Street
The segment of 55th Street between the Metra line and the lake offers a series of ethnic restaurants serving Thai, Japanese, and Korean cuisine. To the west of the Metra line between 54th and 55th streets lies the Hyde Park Shopping Center. The shopping center is anchored by the Treasure Island grocery store, and also includes a Walgreens, Ace Hardware, Office Depot, Potbelly Sandwich Works, the Bonjour Bakery and Cafe, and an upscale French restaurant called "La Petite Folie."
57th Street
57th Street is noted for its independent bookstores, including the South Side branch of Powell's and the general-readership branch of the Seminary Co-op bookstore, known as "57th Street Books." 57th Street also offers the Medici Restaurant and Bakery, Z&H Cafe, and the Salonica Restaurant, along with small grocery stores, hair stylists, and dry cleaners. On the first weekend in June, the venerable 57th Street Art Fair takes up 57th Street between Kimbark and Kenwood avenues.
Museums
- -- DuSable Museum of African American History (located just outside Hyde Park on the eastern edge of Washington Park)
- -- Hyde Park Art Center
- -- Museum of Science and Industry
- -- Oriental Institute – an archaeology museum (mostly focusing on the ancient Near East) within the University of Chicago.
- -- Smart Museum of Art – an art museum within the University of Chicago.
Institutions of Higher Education
- -- Catholic Theological Union – a seminary of Roman Catholic religious orders and lay women and men.
- -- Chicago Theological Seminary – a seminary of the United Church of Christ.
- -- Lutheran School of Theology at Chicago – a seminary of the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America.
- -- McCormick Theological Seminary – a seminary of the Presbyterian Church.
- -- University of Chicago – a private research university.
- -- University of Chicago Laboratory Schools – a private coeducational nursery-12 school founded by educational reformer John Dewey in 1896.
Houses of Worship
- -- St. Thomas Church and Convent
- -- Rockefeller Chapel
- -- First Unitarian Church of Chicago
- -- KAM Isaiah Israel
- -- The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
- -- The First Baptist Church of Chicago the oldest Baptist church in the city
- -- Hyde Park Union Church
- -- Congregation Rodfei Zedek
- -- Rohr Chabad at the University of Chicago and Hyde Park
Transportation
Hyde Park is connected to the rest of the city by CTA buses and the Metra Electric Line. CTA buses provide express service to the downtown, and they also allow transfers to Red Line and Green Line trains to the Loop. The Metra Electric Line, which uses the tracks of the former Illinois Central Railroad, has several stops in Hyde Park and provides service to Millennium Station in the downtown.
CTA bus services
- -- #2 Hyde Park Express
- -- #4 Cottage Grove
- -- #6 Jackson Park Express
- -- #10 Museum of Science and Industry
- -- #15 Jeffery Local
- -- #28 Stony Island
- -- #55 Garfield
Additional CTA bus services, paid for by the University of Chicago
- -- #171 University of Chicago/Hyde Park
- -- #172 University of Chicago/Kenwood
- -- #192 University of Chicago Hospitals Express