Queen's College: Difference between revisions
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
[[File:Map-of-queens-college.jpg]] | [[File:Map-of-queens-college.jpg]] | ||
== Old Wyvern Hall: The Tremere Chantry == | == '''Old Wyvern Hall:''' The Tremere Chantry == | ||
[[File:Wyvern House1.jpg]] | [[File:Wyvern House1.jpg]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 19:46, 25 March 2016
Introduction
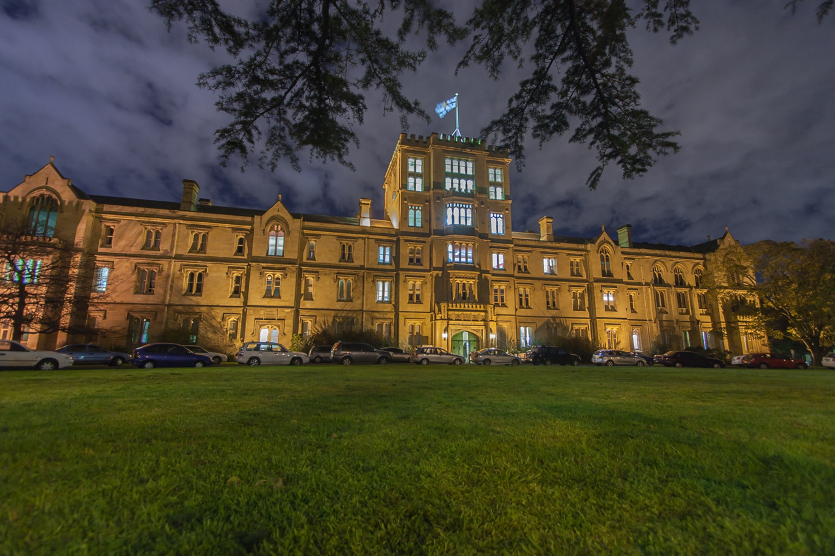
Queen's College is a residential College affiliated with the University of Melbourne providing accommodation to 220 students who are attending the University of Melbourne, Victorian College of the Arts, RMIT University and Monash University Faculty of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences.
In addition to the students, the Queen's College (affectionately known simply as "Queen's") also houses a number of fellows, resident tutors, scholars and professionals (collectively known as the Senior Common Room), staff, and academic guests.
Coat of Arms

The College's coat of arms celebrates its founding as a Methodist institution, in the tradition of the 18th-century Anglican minister, John Wesley.[5] It has the following heraldic description:
- Argent, a cross sable, in each quarter three escallops of the last, for Wesley; on an escutcheon of pretence the Royal Arms of England. Crest: on a wreath and sable, a wyvern proper. Motto: Aedificamus in aeternum.
The actual rendering of the eschutcheon uses not the arms of England, but the arms of the United Kingdom. This is superimposed on the arms of John Wesley.
The college motto translates to We build for eternity.
The arms were assumed without a formal grant from the College of Arms.
History
Founding
The college was founded in 1887, on 10 acres (40,000 m2) of land assigned to the Methodist Church by the Parliament of Victoria in the area then known as University Reserve (now College Crescent). While this land was allocated soon after the founding of the university in 1853, it was not until 1878—some twenty-five years later—that the Methodist Conference took the first steps towards building the college.
The then Governor of Victoria, Sir Henry Brougham Loch, laid the foundation stone on June 16, 1887 after the tireless efforts of Reverend William Abraham Quick, who is widely regarded as the founder of Queen's.
Naming
Initially, it was decided that the college was to be named Victoria College. However, when it became clear that it was to be built in the year of Queen Victoria's golden jubilee, it was finalised in December 1886: "That the new College be called Queen's College in honour of the Queen's Jubilee"
Opening
Queen's opened its doors on March 16, 1889 with a total of 24 students, under the leadership of Rev. Dr. Edward Holdsworth Sugden, who would go on to hold the position of The Master for over forty years. Shortly afterward, it became clear that more building was necessary, and on April 20, 1890, the South Wing was opened. Subsequent extensions were made in 1905, and in 1910 a new East Wing was created, joining the new southern wing with the original sections.
During this time (from 1897 to 1920), it is noted that "Queen's College was a veritable hothouse of dramatic activity", with plays and soirees being performed several times annually. Melbourne University Student Theatre traces its roots to this time, and it is no wonder that promotional posters from these productions still adorn the walls of the college to this day.
Expansion
Post-Great War pressures nurtured additional building plans, advocated mainly by J. T. Tweddle. The central tower (named the Sugden tower after the first master of the college, Rev. Edward J. Holdsworth Sugden) and a new northern wing, known as the Tweddle Wing, were constructed and completed in 1923. 1930 saw the introduction of a scientific laboratory (which now serves as a student recreation centre) in the southern section of the college, courtesy of A. M. and G. R. Nicholas.
From 1958 to 1978, a significant expansion and improvement programme was enacted, partly funded by the Commonwealth Government. The Raynor C. Johnson Wing, named after the college's third Master and erected in the west of the college grounds, was completed in two stages. The first opened in 1961, with the second following eight years later. During the construction of the Johnson Wing, it became clear that the dining hall (which now serves as the Junior Common Room) was too small to contain the projected student body. As such, the current Eakins Hall was built, finished in 1964. The final student accommodation building, Kernick House, was completed in 1975.
In 1964, 3 acres (12,000 m2) of college land was allocated for the creation of a women's college. The college, named St Hilda's is now a coeducational facility, as by the time it was completed Queen's was also accepting both men and women as equal members.
For a decade from 1969, Queen's had also been ensuring that the pre-existing facilities would attain the same standard as the new wing. The resulting "comfortable, single bedroom studies" remain much the same format today. Also around this time, the Methodist Church merged with most parishes of the Presbyterian Church to form the Uniting Church, of which the college thus became an institution.
Coinciding with the College's centenary celebrations, the new Featonby Library and several tutor flats contained in Parnaby Wing were opened in 1987. More recently, the college has focused on expanding accommodation for academic visitors, postgraduate students and resident tutors, with the construction of Scott Terrace(1998), Jack Clarke and Lapthorne buildings (2000). Queen's currently has future plans to extend student accommodation by 2012.
The College Grace
- It is customary to open each formal dinner (held every Monday through Wednesday) at Queen's with a Grace. The college's full Latin grace is as follows
- Domine, qui aperis manum tuam et omnia implentur bonitate,
- Benedicere dignare cibum istum
- Ut nos, ex eo gustantes,
- Inde corporis et animi accipiamus sanitatem.
- Per Jesum Christum Dominum nostrum, Amen.
- An English translation is
- Lord, you open your generous hand
- And the whole world is filled with good things.
- Please bless this food we are about to eat,
- So that we may have healthy bodies and healthy minds,
- Through Jesus Christ our Lord, Amen.
An English grace was composed by Master Henley in 1995, with the proviso that the Latin grace be retained at least once per week.
People associated with Queen's
The Masters of Queen's
- Rev. Edward J. Holdsworth Sugden (1887 - 1928)
- Rev. Frederick Walwyn Kernick (1929 - 1933)
- John F. Foster. (1933 - 1934) - Acting Master
- Raynor Carey Johnson (1934 - 1964)
- Rev. Norman Edgar Lade (1964 - 1965) - Acting Master
- Owen W. Parnaby (1966 - 1986)
- George A. M. Scott, FLS (1986 - 1992)
- Jack William Clarke, OAM (1992) - Acting Master
- Rev. John A. Henley, (1993 - 2001)
- David T. Runia, FAHA (2002–Present)
Wyvern Society
Wyverns are residents, past or present, who have lived in the College for six months or more. The Wyvern Society is responsible for allowing the continued communication of ex-Queen's students, and organising reunions.
- Distinguished Wyverns include
- David Penington (former Vice-Chancellor of the University of Melbourne, former dean of its School of Medicine)
- Sir Roy Wright (former Chancellor of the University of Melbourne)
- Geoffrey Blainey (historian)
- Sir Ian Potter (businessman and philanthropist)
- Harold Holt (former Prime Minister of Australia)
- Brian Howe (former Deputy Prime Minister of Australia)
- Red Symons (musician & comedian)
- Alan Hopgood (writer & actor)
- Sir John Holland (engineer and construction magnate)
- Merlin Crossley (biochemist)
- David Lawrence (comedian)
- Kathy Watt (cyclist)
- Tun Dr Ismail (former Deputy Prime Minister of Malaysia)
- Dato Sri Mustapa Mohamed (current Minister of Trade of Malaysia)
Fellows
Queen’s has a body of 24 Fellows and a smaller body of Honorary Fellows. Fellows of Queen’s College are not actively engaged in teaching the students. Instead, they are men and women who have distinguished themselves through their contributions to academic studies general contributions society. The chief task of the Fellows is to advise the Master on academic affairs and giving of scholarships to students of the College. They are led by the Principal Fellow.
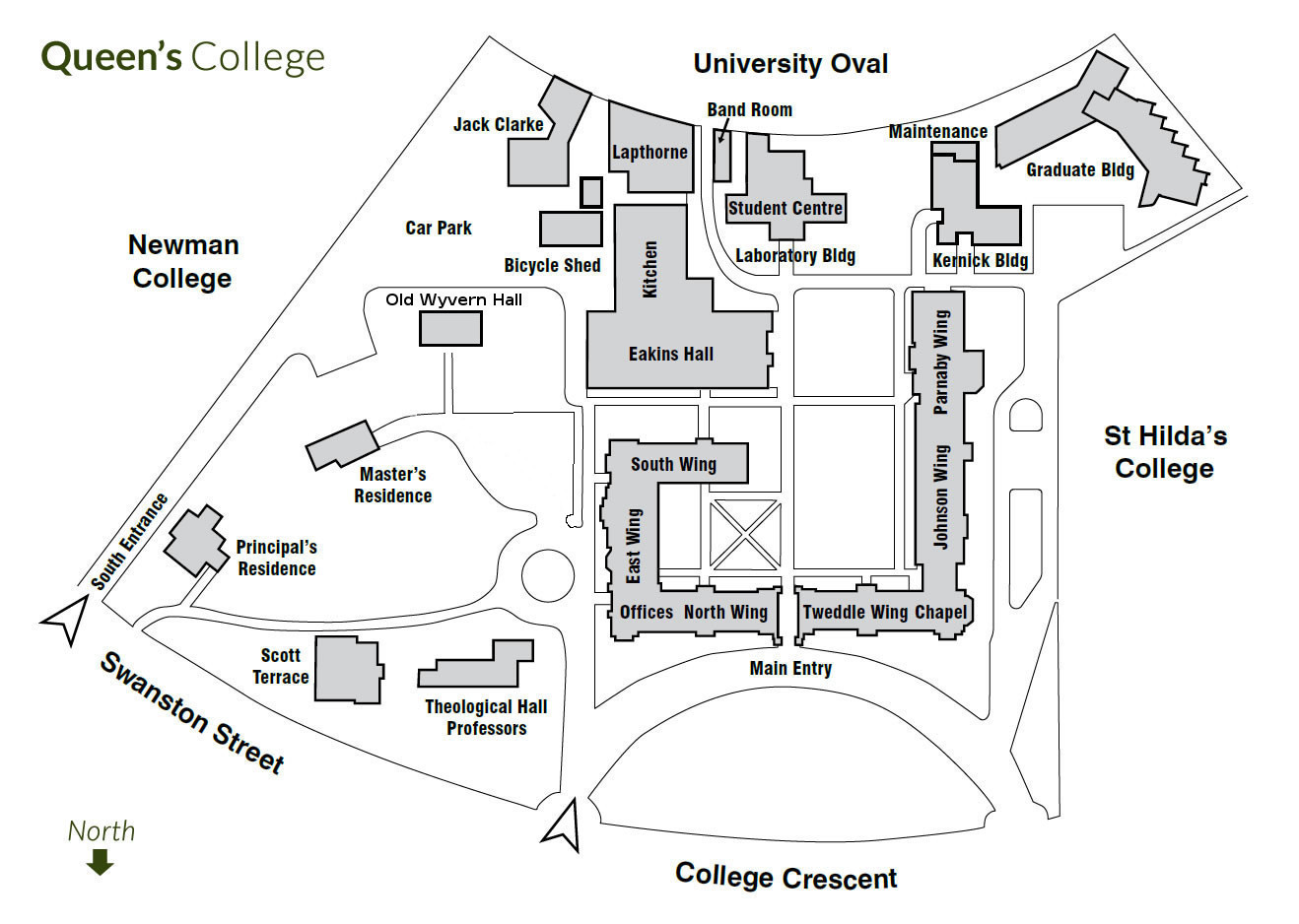
Map of Queen's College
Old Wyvern Hall: The Tremere Chantry
Introduction
While it is uncertain precisely when the Tremere of Melbourne began to influence events at Queen's College, it can be assumed with reasonable certainty to have begun in 1887, the year of Queen Victoria's Golden Jubilee.
History
Architecture
Websites
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Queen's_College_%28University_of_Melbourne%29
http://www.queens.unimelb.edu.au/